I-Rinse Spray
Therapy Area
Respiratory
1.0 Generic name
Saline Nasal Solution IP
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Sodium Chloride IP…………………………. 0.9 % w/v
in Purified Water IP q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Nasal Spray
Sodium Chloride (0.9%w/v)
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
- Gently cleans the nasal cavities when nose is blocked during colds or in allergic conditions.
- Moisturises the nasal mucosa when dry or irritated.
- Thins and loosens nasal secretions and helps their removal.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Method of administration: Nasal use
Infants and toddlers up to 2 years: 1 spray/ nostril or 1-2 drops/nostril.
Adults and children > 2 years: 1-2 spray/ nostril or 2-3 drops/ nostril as needed. The usual frequency of use is 2 to 4 times a day per nostril. I Rinse is suitable for infants, children and adults. Seek medical advice before using I Rinse in an infant less than 2 weeks old. For children below 11 years, I Rinse should be used under adult supervision. For hygienic reasons and to avoid contamination, the nasal spray should be used by one person.
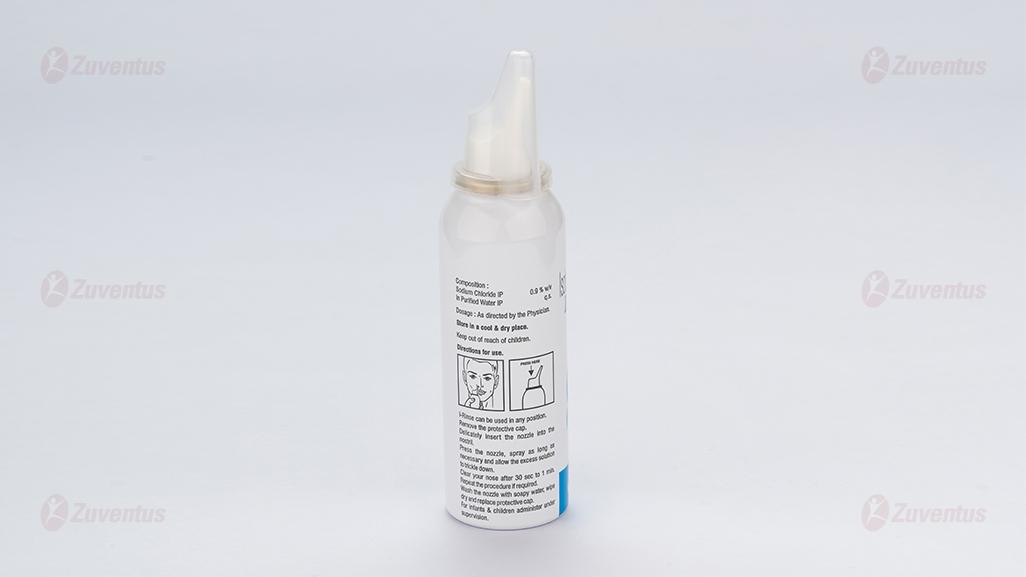
Method of Administration
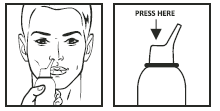
I-Rinse can be used in any position. Remove the protective cap. Delicately insert the nozzle into the nostril. Press the nozzle, spray as long as necessary and allow the excess solution to trickle down. Clear your nose after 30 secs to 1 min. Repeat the procedure if required. Wash the nozzle with soapy water, wipe dry and replace protective cap. For infants & children administer under supervision.
4.3 Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Consult a doctor before use if you are using the product after nasal surgery or injury.
- Due to its cleansing properties, it should be used first when using another local nasal product (e.g. for cold or allergic rhinitis).
- Keep out of reach and sight of Children.
- Do not use a broken, expired or damaged product.
4.5 Drugs interactions
No known drug-drug interaction.
4.6 Use in special populations
I Rinse nasal spray may be used during pregnancy and breast-feeding.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
None known.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Stinging, sneezing increased nasal discharge or salty taste may occur. If any of these effects persists or worsen, notify your doctor. Tell your doctor immediately if frequent nosebleeds occur. If you notice any other effects not listed above, contact your doctor. Reporting of suspected adverse reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product.
Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Treatment should be supportive and systematic.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action/Pharmacodynamic properties
The exact mechanism of action of saline nasal irrigation is unknown. One possibility is that the breakdown of the protective function of the nasal mucosa plays a role in upper respiratory conditions. Saline nasal irrigation may improve nasal mucosa function through several physiologic effects, including direct cleansing, removal of inflammatory mediators and improved mucociliary function, as suggested by increasing ciliary beat frequency.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Sodium chloride distributes primarily to extracellular compartments, including plasma and interstitial fluid; sodium is maintained outside the cell via the Na+/K+-ATPase pump, which exchanges intracellular sodium for extracellular potassium. Penetration across the blood-brain barrier is low. Sodium chloride is excreted primarily in the urine, but it is also excreted in sweat and stool. In healthy patients at steady state with minimal sweat losses, sodium excreted in urine is roughly the same as dietary intake. Sweat sodium concentration is increased in children with cystic fibrosis, aldosterone deficiency, or pseudohypoaldosteronism.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Not available.
7.0 Description
Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. Molecular Weight : 58.44 g/mol.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None known.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
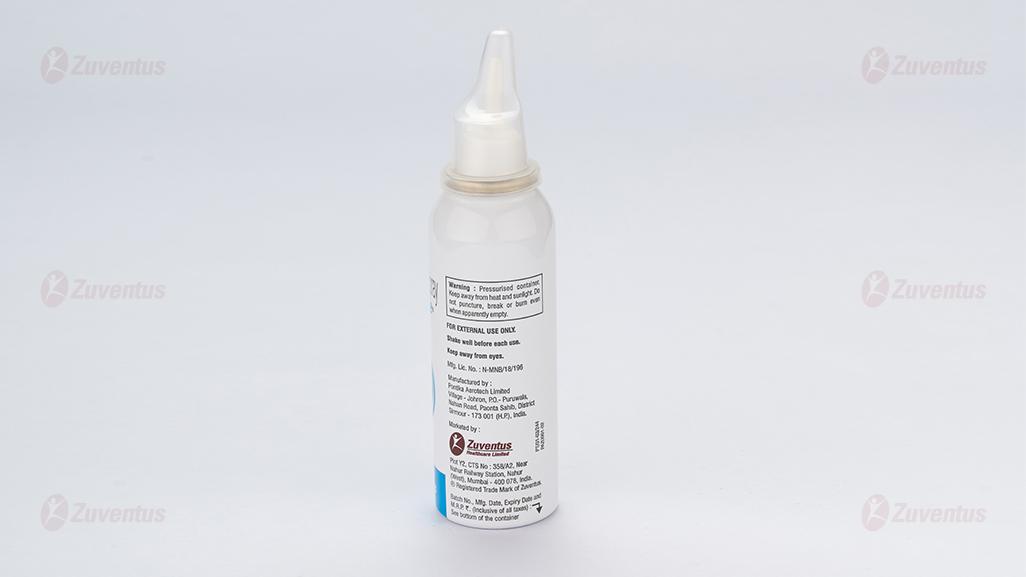
- Pressurised container. Keep away from heat and sunlight.
- Do not puncture, break or burn even when apparently empty.
- For external use only.
- Shake well before each use.
- Keep away from eyes.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
- Shake the bottle before using the medicine.
- Clean your nose thoroughly before using the medicine.
- Insert the bottle tip into one nostril and close the other nostril.
- Direct the spray towards the sides of your nostril, away from the cartilage dividing the two sides of your nose.
- Breathe out gently through your mouth and repeat the same process for the other nostril.
- Avoid deep breathing as it will cause medication to go back to the throat and make it less effective.
- Avoid deep breathing as it will cause the medication to go back to the throat and make it less effective.
- Do not share the bottle with anyone else so that you do not spread germs.
12.0 Date of revision of text
06.01.2025
About Leaflet
Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
- What I-Rinse Nasal Spray is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use I-Rinse Nasal Spray
- How to take I-Rinse Nasal Spray
- Possible side effects
- How to store I-Rinse Nasal Spray
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What I-Rinse Nasal Spray is and what it is used for
I-Rinse Nasal Spray contains saline (sodium chloride 0.9% w/v) in purified water. It is used to:
- Gently clean nasal cavities when the nose is blocked due to colds or allergies.
- Moisturize dry or irritated nasal mucosa.
- Thin and loosen nasal secretions to aid their removal.
2. What you need to know before you use I-Rinse Nasal Spray
Do not use I-Rinse Nasal Spray if:
- You are allergic to sodium chloride or any other ingredients of this medicine.
Warnings and precautions
- Consult a doctor before use if you have had nasal surgery or injury.
- Use I-Rinse first if you are using another local nasal product.
- Keep out of reach of children.
- Do not use if the product is broken, expired, or damaged.
Other medicines and I-Rinse Nasal Spray:
- No known drug interactions.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
I Rinse nasal spray may be used during pregnancy and breast-feeding.
Driving and using machines:
Not available.
3. How to take I-Rinse Nasal Spray
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Dosage:
- Infants and toddlers up to 2 years: 1 spray/nostril or 1-2 drops/nostril.
- Adults and children over 2 years: 1-2 sprays/nostril or 2-3 drops/nostril as needed.
- Use 2 to 4 times a day per nostril.
Method of administration:
- Remove the protective cap.
- Insert the nozzle into the nostril and press to spray.
- Allow excess solution to trickle down and clear your nose after 30 seconds to 1 minute.
- Repeat if necessary.
- Wash the nozzle with soapy water, wipe dry, and replace the cap.
- For infants and children, use under adult supervision.
Other Precautions
- Shake the bottle before using the medicine.
- Clean your nose thoroughly before using the medicine.
- Insert the bottle tip into one nostril and close the other nostril.
- Direct the spray towards the sides of your nostril, away from the cartilage dividing the two sides of your nose.
- Breathe out gently through your mouth and repeat the same process for the other nostril.
- Avoid deep breathing as it will cause medication to go back to the throat and make it less effective.
- Avoid deep breathing as it will cause the medication to go back to the throat and make it less effective.
- Do not share the bottle with anyone else so that you do not spread germs.
If you use more I-Rinse Nasal Spray than you should
Tell your doctor if you accidentally use more than you were told.
If you forget to use I-Rinse Nasal Spray
If you forget to take at the right time, use it as soon as you remember, then carry on as before. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop using I-Rinse Nasal Spray
Do not stop your treatment even if you feel better unless told to do so by your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Common side effects may include:
- Stinging, sneezing, increased nasal discharge, or salty taste.
If any side effects persist or worsen, or if you experience frequent nosebleeds, contact your doctor immediately.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly:
Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store I-Rinse Nasal Spray
- Store in a cool, dry place away from heat and sunlight.
- Do not puncture, break, or burn the container, even when empty.
- Shake well before each use.
- Keep away from eyes.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What I-Rinse Nasal Spray contains:
Ingredients:
- Sodium Chloride IP 0.9% w/v in Purified Water IP q.s.
Revised on 1/25