Monobact Kid Injection
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Generic name
Ceftriaxone & Sulbactam for Injection IP
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
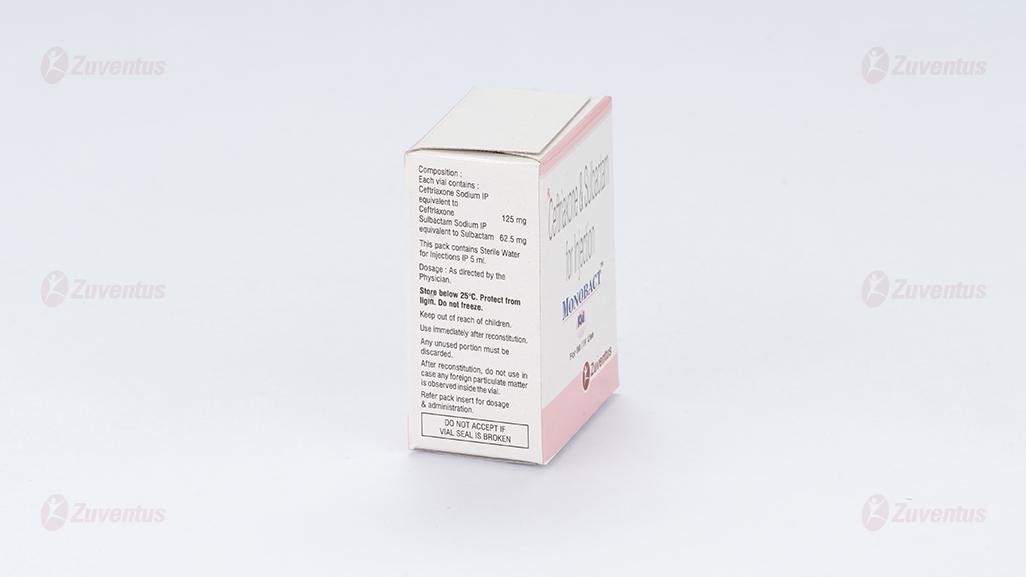
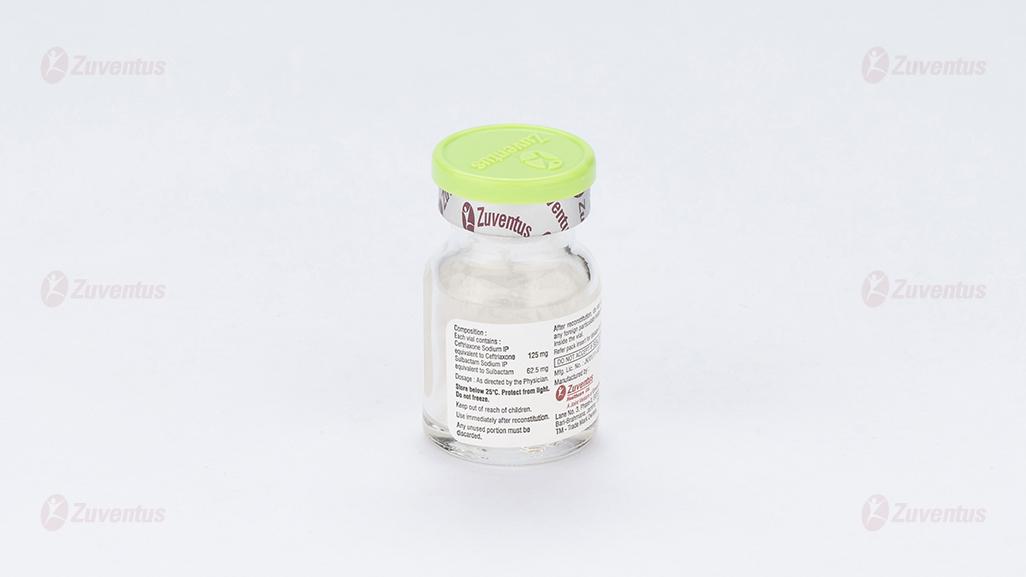
Monobact Kid
Each vial contains :
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 125 mg
Sulbactam Sodium IP equivalent to Sulbactam 62.5 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
Monobact 375 mg
Each vial contains :
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 250 mg
Sulbactam Sodium IP equivalent to Sulbactam 125 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
Monobact 750 mg
Each vial contains :
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 500 mg
Sulbactam Sodium IP equivalent to Sulbactam 250 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
Monobact 1.5 gm
Each vial contains :
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 1000 mg
Sulbactam Sodium IP equivalent to Sulbactam 500 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 10 ml.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Powder for solution for injection.
187.5 mg / 375 mg / 750 mg / 1.5 gm
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
- Bacterial meningitis
- Infections of bones and joints
- Community acquired pneumonia
- Complicated skin and soft tissue infections
- Hospital acquired pneumonia
- Gonorrhoea
- Acute otitis media
- Syphilis
- Intra-abdominal infections
- Bacterial endocarditis
- Complicated urinary tract infections
- Surgical prophylaxis
4.2 Posology and method of administration
To be administered by deep intramuscular (I.M.) injection, slow intravenous (I.V.) injection, or as a slow I.V. infusion, after reconstitution with sterile water for injection (SWFI).
Dosage recommendations in adults
Usual Recommended Dose : 1.5 g to 3 g of Monobact Injection (1 g / 2 g ceftriaxone + 0.5 g / 1 g sulbactam) per day given once a day or in two equally divided doses every 12 hours. The total daily dose of ceftriaxone should not exceed 4 grams. Also, the total dose of sulbactam should not exceed 4 grams per day
For Uncomplicated Gonococcal Infections : A single dose of 750 mg of Monobact Injection (500 mg ceftriaxone + 250 mg sulbactam) to be administered by I.M. route. For Preoperative Use (Surgical Prophylaxis): A single dose of 1.5 g of Monobact Injection (1g ceftriaxone + 0.5 g sulbactam) to be administered intravenously 30 minutes to 2 hours before surgery
The usual duration of therapy is 4 to 14 days. In complicated infections, longer therapy may be required. Or, as prescribed by the physician.
Dosage in adult patients with renal impairment and hepatic dysfunction
In patients with both hepatic dysfunction and significant renal disease, caution should be exercised and the ceftriaxone dosage should not exceed 2 grams daily. Dose of sulbactam should be adjusted in patients with marked decrease in renal function (creatinine clearance of < 30 ml/min) and to compensate for reduced clearance less than 15ml/min, maximum dose of sulbactam should not exceed 1 gram per day.
Dosage recommendations in pediatric patients
For children with bodyweight above 50 kg or age over 12 years, the usual adult dosage should be administered. Although, ceftriaxone can be administered in neonates and infants, the safety and efficacy of this combination product (ceftriaxone + sulbactam injection) has not been established in children below 1 year of age. Thus, Monobact Injection is recommended only in pediatric patients 1 year of age or older.
Following doses in children are expressed in terms of ceftriaxone content of the formulation. Usual Recommended Dosage : 50 to 75 mg/kg/day, given in divided doses every 12 hours. The total daily dose of ceftriaxone should not exceed 2 grams. Sulbactam dose in children should not exceed 100 mg/kg/day.
Treatment of Meningitis : The initial therapeutic dose should be 100 mg/kg body weight. Thereafter, daily dose of 100 mg/kg may be administered once a day or in equally divided doses every 12 hours. The total daily dose of ceftriaxone should not exceed 4 grams. The usual duration of therapy is 7 to 14 days depending on the type and severity of infection. Or, as prescribed by the physician
Geriatric patients
Dosage adjustments are not necessary for geriatric patients with ceftriaxone dosages up to 2 grams per day provided there is no severe renal and hepatic impairment.
Pharmaceutical precautions
Ceftriaxone-containing injection should not be mixed with other drugs in infusion bottle since compatibility has not been established. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Directions for reconstitution and dilution for use
Monobact comes in a composite pack containing one vial of dry powder and Sterile Water for Injections IP in ampoule. Each Monobact 1.5 gm pack contains 1 ampoule of 10 ml Sterile Water for Injections IP [SWFI]. Monobact 750 mg contains 1 ampoule of 5 ml Sterile Water for Injections IP, Monobact 375 mg and Monobact Kid packs contain 1 ampoule of 5 ml Sterile Water for Injections IP per pack. SWFI IP from the ampoule should be used to dissolve the dry powder present in the vial, just prior to the use. After adding the SWFI IP into the vial, agitate the vial gently until the powder dissolves completely into the solution.
Though, stability studies have shown that the solution is stable for 24 hrs at 25°C and up to days under 2°C to 8°C. It is advisable to use the solution immediately after reconstitution. Following are the recommendation for diluting the solution

4.3 Contraindications
- In patients with known hypersensitivity to ceftriaxone, cephalosporin class of antibiotics, or to tazobactam or to any component of the formulation.
- In hyperbilirubinemic neonates/preterm newborns : Ceftriaxone can displace bilirubin from its binding to serum albumin, leading to a risk of bilirubin encephalopathy in these patients.
- Premature neonates : Ceftriaxone is contraindicated in premature neonates up to a postmenstrual age of 41 weeks (gestational age + chronological age).
- In neonates (≤ 28 days) if they require (or are expected to require) treatment with calcium-containing I.V. solutions, including continuous calcium-containing infusions such as parenteral nutrition because of the risk of precipitation of ceftriaxone-calcium.
- Intravenous administration of ceftriaxone solutions containing lidocaine is contraindicated.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions
Test dose
Hypersensitivity
Before initiation of therapy, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins and other beta-lactam agents or other drugs. As with all beta-lactam antibacterial agents, serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity reactions (i.e., anaphylaxis) have been reported. In case of severe hypersensitivity reactions, treatment with ceftriaxone must be discontinued immediately and adequate emergency measures must be initiated.
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD)
CDAD has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including ceftriaxone, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Hemolytic anemia
An immune mediated hemolytic anemia has been observed in patients receiving cephalosporin class of antibacterial drugs including ceftriaxone. Severe cases of hemolytic anemia, including fatalities, have been reported during treatment in both adults and children. If a patient develops anemia while on ceftriaxone, the diagnosis of a cephalosporin associated anemia should be considered and ceftriaxone stopped until the etiology is determined.
Development of drug-resistant bacteria
Prescribing ceftriaxone in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria. Prolonged use of ceftriaxone may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Pancreatitis
Cases of pancreatitis, possibly secondary to biliary obstruction, have been reported in patients treated with ceftriaxone. Most patients presented with risk factors for biliary stasis and biliary sludge (preceding major therapy, severe illness, and total parenteral nutrition). A cofactor role of ceftriaxone-related biliary precipitation cannot be ruled out.
Urolithiasis and post-renal acute renal failure
Ceftriaxone-calcium precipitates in the urinary tract have been observed in patients receiving ceftriaxone. The probability of such precipitates appears to be greatest in pediatric patients. Patients may be asymptomatic or may develop symptoms of urolithiasis, and ureteral obstruction and post-renal acute renal failure. The condition appears to be reversible upon discontinuation of ceftriaxone and institution of appropriate management. Ensure adequate hydration in patients receiving ceftriaxone. Discontinue ceftriaxone in patients who develop signs and symptoms suggestive of urolithiasis, oliguria or renal failure and/or the sonographic findings.
Gallbladder pseudolithiasis
Ceftriaxone-calcium precipitates in the gallbladder have been observed in patients receiving ceftriaxone. The probability of such precipitates appears to be greatest in pediatric patients. Patients may be asymptomatic or may develop symptoms of gallbladder disease. The condition appears to be reversible upon discontinuation of ceftriaxone and institution of conservative management. Discontinue ceftriaxone sodium in patients who develop signs and symptoms suggestive of gallbladder disease and/or the sonographic findings.
Effect on prothrombin time
Alterations in prothrombin times have occurred in patients treated with ceftriaxone. Monitor prothrombin time during ceftriaxone treatment in patients with impaired vitamin K synthesis or low vitamin K stores (e.g., chronic hepatic disease and malnutrition). Vitamin K administration (10 mg weekly) may be necessary if the prothrombin time is prolonged before or during therapy.
Altered laboratory tests
Positive direct Coombs' test and galactosemia test, false-positive test for urinary glucose and elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
4.5 Drug interactions
Ceftriaxone
Amsacrine, Vancomycin, Fluconazole, and Aminoglycosides : Ceftriaxone is incompatible with these drugs.
Oral Contraceptives : Ceftriaxone may adversely affect the efficacy of oral hormonal contraceptives. Consequently, it is advisable to use supplementary (non-hormonal) contraceptive measures during treatment and in the month following treatment. Chloramphenicol : Caution is advised if concurrent administration of ceftriaxone with chloramphenicol is proposed.
Vitamin K Antagonist : Concomitant use of ceftriaxone with vitamin K antagonists may increase the risk of bleeding. Coagulation parameters should be monitored frequently, and the dose of the anticoagulant adjusted accordingly, both during and after treatment with ceftriaxone.
Sulbactam
Probenecid : Probenecid decreases the renal tubular secretion of sulbactam. Concurrent use of probenecid with sulbactam may result in increased and prolonged blood levels of sulbactam.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Animal studies have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, Monobact Injection should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Lactation
Although sulbactam is distributed into breast milk in small amounts, no adverse effects have been seen in breast-fed infants and it is usually compatible with breast feeding. Low concentration of ceftriaxone is excreted in human milk. Therefore, caution should be exercised when Monobact Injection is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric patients
Safety and effectiveness of ceftriaxone has been established in pediatric patients. In vitro studies have shown that ceftriaxone, like some other cephalosporins, can displace bilirubin from serum albumin. Thus, ceftriaxone-containing preparations should not be administered to hyperbilirubinemic children. Safety and efficacy of Monobact Injection has not been established in children below 1 year of age.
4.7 Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
During treatment undesirable effects such as dizziness, headache, and convulsions may occur, which may influence the ability to drive and use machines. If affected by such events, patients should not drive or operate machinery.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Ceftriaxone-containing preparations are generally well tolerated. In clinical trials, the following adverse reactions were observed (related to ceftriaxone therapy or of uncertain etiology). Local Reactions : Injection site pain, induration, tenderness, phlebitis, warmth, tightness. Hypersensitivity : Rash, pruritus, fever or chills.
Infections and Infestations : Genital fungal infection. Hematologic : Eosinophilia, thrombocytosis, leukopenia. Less frequently reported were anemia, hemolytic anemia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia and prolongation of the prothrombin time.
Blood and Lymphatic Disorders : Granulocytopenia, coagulopathy. Gastrointestinal : Diarrhea/loose stools, nausea, vomiting, dysgeusia, pseudomembranous colitis.
Hepatic : Elevations of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin.
Renal : Elevations of the blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine and the presence of casts in the urine.
Central Nervous System : Headache, dizziness.
Dermatologic : Exanthema, allergic dermatitis, urticaria, edema; acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) and isolated cases of severe cutaneous adverse reactions (erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome or Lyell's syndrome / toxic epidermal necrolysis) have been reported.
Miscellaneous : Diaphoresis, flushing, increased blood creatinine.
Other rarely observed adverse reactions (< 0.1%) include abdominal pain, agranulocytosis, allergic pneumonitis, anaphylaxis, basophilia, biliary lithiasis, bronchospasm, colitis, dyspepsia, epistaxis, flatulence, gallbladder sludge, glycosuria, hematuria, jaundice, leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, monocytosis, nephrolithiasis, palpitations, decrease in the prothrombin time, renal precipitations, seizures, and serum sickness.
Reporting of side effects
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via
email to : medico@zuventus.com
Website : https://www.zuventus.co.in/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
In the case of overdose nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea can occur. There is no specific antidote. Treatment should be supportive and symptomatic according the patient's clinical presentation.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone is a third generation cephalosporin class of beta-lactam antibiotic. Ceftriaxone inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis and produces bactericidal effect. Ceftriaxone has activity in the presence of some beta-lactamases, both penicillinases and cephalosporinases, of Gramnegative and Gram-positive bacteria.
Sulbactam
Beta-lactamases are the enzymes produced by certain bacteria to develop resistant to penicillin and cephalosporin class of beta-lactam antibiotics. Sulbactam inhibits action of these enzymes irreversibly. In particular, sulbactam has good inhibitory activity against the clinically important plasmid mediated beta-lactamases most frequently responsible for transferred drug resistance. The addition of sulbactam effectively extends the antibacterial spectrum of concurrently administered beta-lactam antibiotic (e.g., ceftriaxone) to include many bacteria normally resistant to it.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
The combination of ceftriaxone and sulbactam is active against wide variety of beta-lactamase producing gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In addition, it demonstrates synergistic activity (reduction in MICs of combination therapy versus ceftriaxone alone) in a variety of organisms which are sensitive to ceftriaxone.
Monobact Injection has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following bacteria, both in vitro and in clinical infections :
Gram-negative Bacteria
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus Moraxella catarrhalis
Enterobacter aerogenes Morganella morganii
Enterobacter cloacae Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Escherichia coli Neisseria meningitidis
Haemophilus influenzae Proteus mirabilis
Haemophilus parainfluenzae Proteus vulgaris
Klebsiella oxytoca Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Klebsiella pneumoniae Serratia marcescens
Gram-positive Bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus pyogenes
Staphylococcus epidermidis Viridans group streptococci
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Anaerobic Bacteria
Bacteroides fragilis Peptostreptococcus species
Clostridium species
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90% of the following microorganisms exhibit an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for ceftriaxone. However, the efficacy of ceftriaxone in treating clinical infections due to these microorganisms has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Gram-negative Bacteria
Citrobacter diversus Salmonella species (including Citrobacter freundii Salmonella typhi)
Providencia species (including Providencia rettgeri) Shigella species
Gram-positive Bacteria
Streptococcus agalactiae
Anaerobic Bacteria
Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) melaninogenicus Prevotella (Bacteroides) bivius
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Ceftriaxone
Absorption : Following intramuscular injection, mean peak plasma ceftriaxone levels are approximately half those observed after intravenous administration of an equivalent dose. The maximum plasma concentration after a single intramuscular dose of 1 gram is about 81 mg/l and is reached in 2 to 3 hours after administration. The area under the plasma concentrationtime curve after intramuscular administration is equivalent to that after intravenous administration of an equivalent dose.
After intravenous bolus administration of ceftriaxone 500 mg and 1 g, mean peak plasma ceftriaxone (Cmax) levels are approximately 120 and 200 mg/l respectively. After intravenous infusion of ceftriaxone 500 mg, 1 g and 2 g, the plasma ceftriaxone levels are approximately 80, 150 and 250 mg/l respectively. An 8 to 15 % increase in Cmax is seen on repeated administration; steady state is reached in most cases within 48 to 72 hours depending on the route of administration.
Distribution : The volume of distribution of ceftriaxone is 7 to 12 litre. Ceftriaxone is reversibly bound to albumin. Plasma protein binding is about 95 % at plasma concentrations below 100 mg/l.
Binding is saturable and the bound portion decreases with rising concentration (up to 85 % at a plasma concentration of 300 mg/l).
Metabolism : Ceftriaxone is not metabolized systemically; but is converted to inactive metabolites by the gut flora. Elimination : Plasma clearance of total ceftriaxone (bound and unbound) is 10 to 22 ml/min. Renal clearance is 5 to 12 ml/min. 50 to 60 % of ceftriaxone is excreted unchanged in the urine, primarily by glomerular filtration, while 40 to 50 % is excreted unchanged in the bile. The elimination half-life of total ceftriaxone in adults is about 8 hours.
Sulbactam
After a 30-minute infusion of 1g of sulbactam, a peak concentration of approximately 43 mcg/ml is obtained. Plasma protein binding is approximately 38%. The mean serum half-life of sulbactam is approximately 1 hour in healthy volunteers. Approximately 75 to 85% of sulbactam is excreted unchanged in the urine during the first 8 hours after administration to individuals with normal renal function.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
Ceftriaxone
LD50 values after administration of ceftriaxone by intravenous route were in mice 1840 mg/kg, in rat 2240 mg/kg, and in rabbit 240 mg/kg. LD50 value reported after administration of ceftriaxone by oral route in mice and rats was >10,000 mg/kg. In a 2-week intravenous administration study, groups of eight male Füllinsdorf rats were administered 0, 25 or 60 mg/kg/day of ceftriaxone. Body weight gain was slightly depressed by 9.2 and 20.1% in the 25 and 60 mg/kg/day groups respectively. The average weight of the thyroid glands was increased in the treated groups by 11 to 14% in comparison to the control animals. A 50% reduction in plasma bilirubin in the treated rats was reported along with a decrease in the number of leucocytes. 11 Genetic toxicology tests included the Ames test, a micronucleus test and a test for chromosomal aberrations in human lymphocytes cultured in vitro with ceftriaxone. Ceftriaxone showed no potential for mutagenic activity in these studies. Carcinogenicity studies on ceftriaxone were not conducted. Reproductive studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses up to 20 times the usual human dose and have no evidence of embryotoxicity, fetotoxicity or teratogenicity. In primates, no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity was demonstrated at a dose approximately 3 times the human dose. Ceftriaxone produced no impairment of fertility when given intravenously to rats at daily doses up to 586 mg/kg/day, approximately 20 times the recommended clinical dose of 2 g/day.
Sulbactam
Relevant data is not available.
7.0 Description
Monobact is a combination of Ceftriaxone Sodium and Sulbactam Sodium available as dry powder for reconstitution.
Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone is a beta-lactam, third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic with bactericidal activity. Molecular Weight : 554.6g/mol.
Molecular Formula : C18H18N8O7S3.
Chemical Name : (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetyl] amino]- 3-[(2-methyl-5,6-dioxo-1H-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1- azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid.
Sulbactam sodium
Sulbactam is a β-lactamase inhibitor given in combination with β-lactam antibiotics to inhibit β- lactamase, an enzyme produced by bacteria that destroys antibiotic activity. Sulbactam sodium is a derivative of the basic penicillin nucleus. Molecular Weight : 255.22 g/mol.
Molecular Formula : C8H10NNaO5S.
Chemical Name : Sodium (2S, 5R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia- 1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane- 2- carboxylate 4,4- dioxide.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Do not use diluents containing calcium, such as Ringer's solution or Hartmann's solution, to reconstitute or to further dilute a reconstituted vial for I.V. administration because a precipitate can form. Precipitation of ceftriaxone-calcium can also occur when ceftriaxone is mixed with calcium-containing solutions in the same I.V. administration line. Ceftriaxone with sulbactam must not be administered simultaneously with calcium-containing I.V. solutions, including continuous calcium-containing infusions such as parenteral nutrition.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
Monobact Kid : A vial of 187.5 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
Monobact 375 mg : A vial of 375 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
Monobact 750 mg : A vial of 750 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
Monobact 1.5 gm : A vial of 1.5 gm with SWFI IP 10 ml.
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store below 25°C. Protect from light. Do not freeze.
Keep out of reach of children. After reconstitution, do not use in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
9.0 Patient counselling information
- Instruct patient to store medication as advised and not to expose the vial to moisture or direct light.
- When ceftriaxone with sulbactam is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may decrease the effectiveness of therapy and increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop antimicrobial resistance.
- Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools even as late as two months after the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, instruct patients to contact their physician immediately.
- Instruct patient not to freeze the reconstituted solution and use it immediately after the preparation. Unused portion of solution, if any, should be discarded.
12.0 Date of revision
16 August 2024
About leaflet
The name of your medicine is Monobact injection. We refer to them as Monobact injection or Monobact throughout this leaflet.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What MONOBACT injection is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you are given MONOBACT injection
3. How MONOBACT injection is given
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store MONOBACT injection
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What MONOBACT injection is and what it is used for
MONOBACT injection is an antibiotic given to adults and children including new-born babies. It contains a combination of antibiotics such as Sulbactam & Ceftriaxone. Sulbactam is a β-lactamase inhibitor whereas Ceftriaxone is a third-generation semi-synthetic cephalosporin. It works by killing bacteria that cause infections. It belongs to a group of medicines called cephalosporins. MONOBACT injection is used for the treatment of:
- Lower Respiratory Tract infections like pneumonia, bronchitis etc.
- Skin and Skin Structure Infections
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Bone and Joint Infections
- Infection coverings of brain (meningitis)
- Use before surgery to prevent infection
- Internal Ear infection
- Urinary Tract Infections
- Bacterial Sepsis (severe infection)
- Intra-Abdominal Infections
- Uncomplicated gonorrhoea, Syphilis (sexually transmitted infection)
2. What you need to know before you are given MONOBACT injection
You must not be given MONOBACT injection if you have:
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance, to any other cephalosporin or to any of the excipients listed in the formulation.
- History of severe hypersensitivity (e.g. anaphylactic reaction) to any other type of beta-lactam antibacterial agent (penicillins, monobactams and carbapenems).
- Premature neonates up to a postmenstrual age of 41 weeks (gestational age + chronological age)
- Full-term neonates (up to 28 days of age):
with hyper-bilirubinaemia, jaundice, or who are hypo-albuminaemic or acidotic because these are conditions in which bilirubin binding is likely to be impaired.
if they require (or are expected to require) intravenous calcium treatment, or calcium-containing infusions due to the risk of precipitation of a ceftriaxone-calcium salt
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist or nurse before you are given MONOBACT injection if:
- You experience serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions. These reactions are more apt to occur in individual with history of hypersensitivity reactions to multiple allergens.
- You have biliary obstruction, liver or kidney problems.
- You have other illnesses, such as vitamin K deficiency
If you need a blood or urine test
Ceftriaxone can affect the results of urine tests for sugar and a give false positive results. If you are having tests:
- Tell the person taking the sample that you have been given MONOBACT injection.
MONOBACT in babies:
- MONOBACT injection has been effectively used in infants
- It has not been extensively studied in premature infants or neonates. Thus, your doctor will decide if MONOBACT can be given in such babies, on the basis of potential benefits and possible risks involved before instituting therapy.
Other medicines and MONOBACT
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
In particular, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking:
- Alcohol
Pregnancy and breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine. The doctor will consider the benefit of treating you with MONOBACT against the risk to your baby.
Driving and using machines
Clinical experience with MONOBACT indicates that it is unlikely to impair a patient's ability to drive or use machinery.
3. How MONOBACT injection is given
MONOBACT injection is usually given by a doctor or nurse. It can be given as a drip (intravenous infusion) or as an injection directly into a vein or into a muscle.
The usual dose
Your doctor will decide the correct dose of MONOBACT for you. The dose will depend on the severity and type of infection; whether you are on any other antibiotics; your weight and age; how well your kidneys and liver are working. The number of days or weeks that you are given MONOBACT depends on what sort of infection you have.
Adults
2 to 4 gram is given in equally divided doses twice a day depending on the severity and type of infection.
If you have a severe infection, your doctor will give you a higher dose (up to 8 grams in equally divided doses twice a day). The recommended maximum daily dosage of Sulbactam is 4 grams (8 gram of Ceftriaxone-Sulbactam).
Children aged > 7 days
The usual dosage of MONOBACT in children is 40 to 80 mg/kg/day (i.e. 20 to 40 mg/kg/day of Ceftriaxone activity) in 2 to 4 equally divided doses, depending on the severity and type of infection. If you have a severe infection, your doctor will give you a higher dose up to 160 mg/kg/day of MONOBACT in 2 to 4 equally divided doses.
Newborn babies (0-7 days)
For neonates in the first week of life, MONOBACT will be given every 12 hours. The maximum daily dosage of Sulbactam in these patients should not exceed 80 mg/kg/day (160 mg/kg/day MONOBACT). In cases where dose above 80 mg/kg/day of Ceftriaxone are necessary, additional Ceftriaxone will be administered separately.
People with liver and kidney problems
You may be given a different dose to the usual dose. Your doctor will decide how much MONOBACT you will need and will check you closely depending on the severity of the liver and kidney disease.
If you are given more MONOBACT than you should
If you accidentally receive more than your prescribed dose, contact your doctor or nearest hospital straight away.
If you forget to use MONOBACT injection
If you miss an injection, you should have it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next injection, skip the missed injection. Do not take a double dose (two injections at the same time) to make up for a missed dose.
If you stop using MONOBACT injection
Do not stop taking MONOBACT injection unless your doctor tells you to. If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects may happen with this medicine:
Local Reactions: pain, induration and tenderness and phlebitis. The incidence of warmth, tightness or induration after Intra Muscular injection.
Hypersensitivity: rash, less frequently reported were pruritus, fever or chills.
Hematologic: eosinophilia, thrombocytosis and leukopenia. Less frequently reported were anemia, haemolytic anemia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia and prolongation of the prothrombin time.
Gastrointestinal: diarrhea. Less frequently reported were nausea or vomiting, and loss of taste. The onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibacterial treatment
Hepatic: elevations of liver enzymes. Less frequently reported were elevations of alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin.
Renal: elevations of the blood urea. Less frequently reported were elevations of creatinine and the presence of casts in the urine.
Central Nervous System: headache or dizziness were reported occasionally.
Genitourinary: Fungal infections were reported occasionally.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Fixed Drug Eruption.
Miscellaneous: diaphoresis and flushing were reported occasionally.
Other rarely observed adverse reactions include abdominal pain, agranulocytosis, allergic pneumonitis, anaphylaxis, basophilia, biliary lithiasis, bronchospasm, colitis, dyspepsia, epistaxis, flatulence, gallbladder sludge, glycosuria, hematuria, jaundice, leucocytosis, lymphocytosis, monocytosis, nephrolithiasis, palpitations, a decrease in the prothrombin time, renal precipitations, seizures, and serum sickness.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store MONOBACT injection
Keep out of the sight and reach of children. Protect from light. After reconstitution, do not use it in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
Do not use MONOBACT injection after the expiry date which is printed on the label and carton.
Do not store above 25°C. Your doctor, pharmacist or nurse will know how to store MONOBACT Injection properly.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What MONOBACT injection contains
The active substance in MONOBACT injection is Ceftriaxone and Sulbactam.
MONOBACT Kid
Each vial contains:
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 125 mg
Sulbactam Sodium IP equivalent to Sulbactam 62.5 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
MONOBACT 375 mg
Each vial contains:
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 250 mg
Sulbactam Sodium IP equivalent to Sulbactam 125 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
MONOBACT 750 mg
Each vial contains:
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 500 mg
Sulbactam Sodium IP equivalent to Sulbactam 250 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
MONOBACT 1.5 gm
Each vial contains: Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 1000 mg
Sulbactam Sodium IP equivalent to Sulbactam 500 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 10 ml.
Pack size/presentation
MONOBACT Kid: A vial of 187.5 mg with sterile water for injection IP 5 ml.
MONOBACT 375 mg: A vial of 375 mg with sterile water for injection IP 5 ml.
MONOBACT 750 mg: A vial of 750 mg with sterile water for injection IP 5 ml.
MONOBACT 1.5 gm: A vial of 1.5 gm with sterile water for injection IP 10 ml.