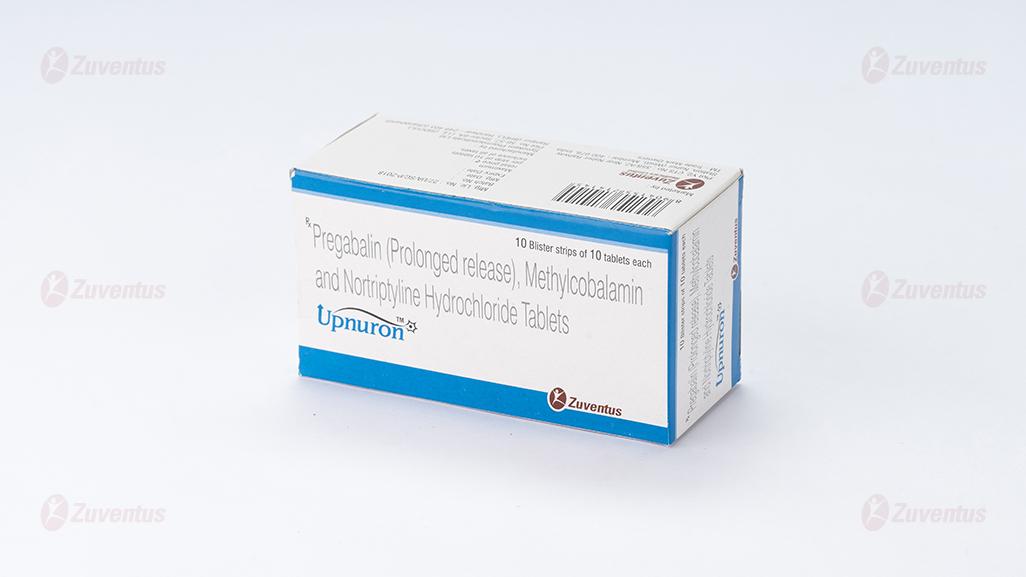
Upnuron Tablets
Therapy Area
Pain management
1.0 Generic Name
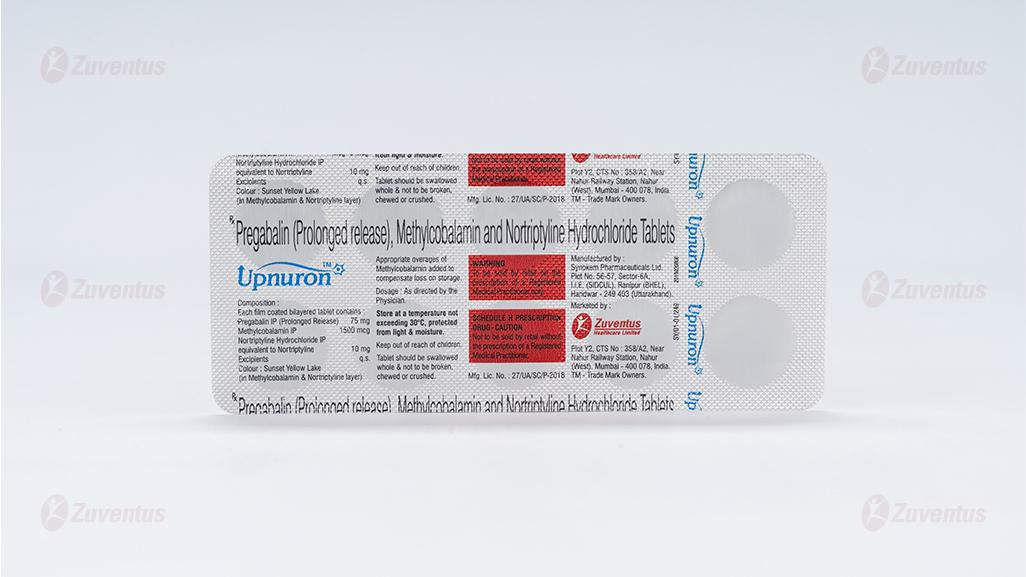
Pregabalin (Prolonged release), Methylcobalamin and Nortriptyline Hydrochloride Tablets
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
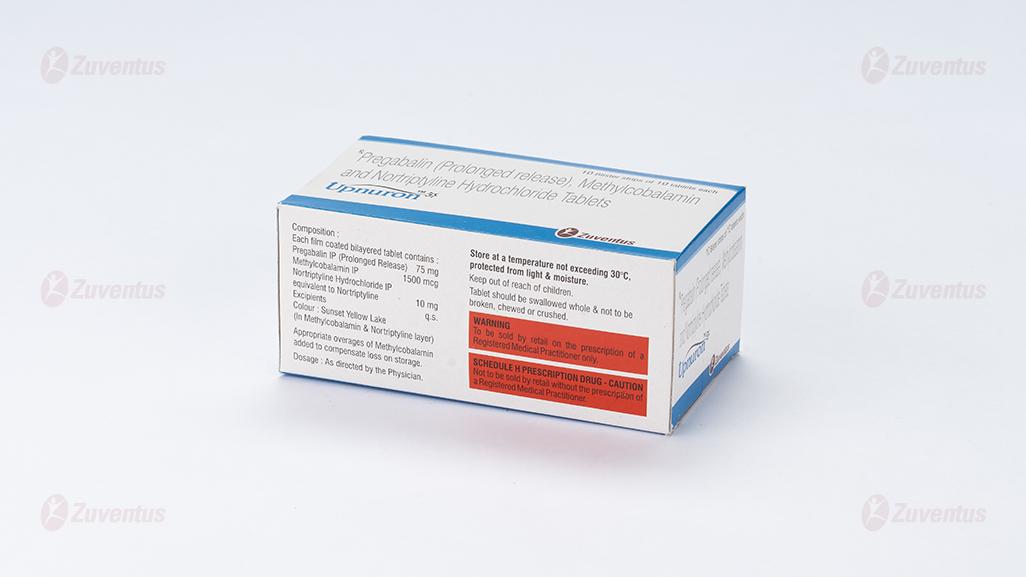
Each film coated bilayered tablet contains :
Pregabalin IP (Prolonged Release) 75 mg
Methylcobalamin IP 1500 mcg
Nortriptyline Hydrochloride IP
equivalent to Nortriptyline 10 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Sunset Yellow Lake (In Methylcobalamin & Nortriptyline layer)
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Bilayered Film Coated Tablets
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of patient with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain with coexistent Vitamin B12 Deficiency.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
One tablet daily or as directed by the Physician Route of Administration : To be taken orally
4.3 Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to any of the active constituents.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Nortriptyline
Patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), both adult and pediatric, may experience worsening of their depression and/or the emergence of suicidal ideation and behaviour (suicidality) or unusual changes in behaviour, whether or not they are taking antidepressant medications, and this risk may persist until significant remission occurs. Suicide is a known risk of depression and certain other psychiatric disorders, and these disorders themselves are the strongest predictors of suicide. There has been a long-standing concern, however, that antidepressants may have a role in inducing worsening of depression and the emergence of suicidality in certain patients during the early phases of treatment. Pooled analyses of short-term placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and others) showed that these drugs increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behaviour (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults (ages 18-24) with major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older.
Pregabalin
Diabetic patients In accordance with current clinical practice, some diabetic patients who gain weight on pregabalin treatment may need to adjust hypoglycaemic medicinal products.
Hypersensitivity reactions
There have been reports in the post-marketing experience of hypersensitivity reactions, including cases of angioedema. Pregabalin should be discontinued immediately if symptoms of angioedema, such as facial, perioral, or upper airway swelling occur. Dizziness, somnolence, loss of consciousness, confusion, and mental impairment Pregabalin treatment has been associated with dizziness and somnolence, which could increase the occurrence of accidental injury (fall) in the elderly population. There have also been postmarketing reports of loss of consciousness, confusion and mental impairment. Therefore, patients should be advised to exercise caution until they are familiar with the potential effects of the medicinal product.
Vision-related effects
In controlled trials, a higher proportion of patients treated with pregabalin reported blurred vision than did patients treated with placebo which resolved in a majority of cases with continued dosing. In the clinical studies where ophthalmologic testing was conducted, the incidence of visual acuity reduction and visual field changes was greater in pregabalin-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients; the incidence of fundoscopic changes was greater in placebo-treated patients. In the post-marketing experience, visual adverse reactions have also been reported, including loss of vision, visual blurring or other changes of visual acuity, many of which were transient. Discontinuation of pregabalin may result in resolution or improvement of these visual symptoms.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Mecobalamin
No known drug interaction
Pregabalin
Since pregabalin is predominantly excreted unchanged in the urine, undergoes negligible metabolism in humans (< 2% of a dose recovered in urine as metabolites), does not inhibit drug metabolism in vitro, and is not bound to plasma proteins, it is unlikely to produce, or be subject to, pharmacokinetic interactions.
In vivo studies and population pharmacokinetic analysis
Accordingly, in in vivo studies no clinically relevant pharmacokinetic interactions were observed between pregabalin and phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproic acid, lamotrigine, gabapentin, lorazepam, oxycodone or ethanol. Population pharmacokinetic analysis indicated that oral antidiabetics, diuretics, insulin, phenobarbital, tiagabine and topiramate had no clinically significant effect on pregabalin clearance.
Oral contraceptives, norethisterone and/or ethinyloestradiol
Co-administration of pregabalin with the oral contraceptives norethisterone and/or ethinyloestradiol does not influence the steady-state pharmacokinetics of either substance.
Central nervous system influencing medical products
Pregabalin may potentiate the effects of ethanol and lorazepam. In controlled clinical trials, multiple oral doses of pregabalin co-administered with oxycodone, lorazepam, or ethanol did not result in clinically important effects on respiration. In the postmarketing experience, there are reports of respiratory failure and coma in patients taking pregabalin and other central nervous system (CNS) depressant medicinal products. Pregabalin appears to be additive in the impairment of cognitive and gross motor function caused by oxycodone.
Interactions and the elderly
No specific pharmacodynamic interaction studies were conducted in elderly volunteers. Interaction studies have only been performed in adults
Nortriptyline HCL
Administration of reserpine during therapy with a tricyclic antidepressant has been shown to produce a “stimulating” effect in some depressed patients. Close supervision and careful adjustment of the dosage are required when nortriptyline HCl is used with other anticholinergic drugs and sympathomimetic drugs. Concurrent administration of cimetidine and tricyclic antidepressants can produce clinically significant increases in the plasma concentrations of the tricyclic antidepressant. The patient should be informed that the response to alcohol may be exaggerated. A case of significant hypoglycemia has been reported in a type II diabetic patient maintained on chlorpropamide (250 mg/day), after the addition of nortriptyline (125 mg/day).
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
There are no adequate data from the use of pregabalin in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity. The potential risk for humans is unknown.
Women of child bearing potential / Contraception in males and females As the potential risk for humans is unknown, effective contraception must be used in women of child bearing potential.
Pregabalin should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary (if the benefit to the mother clearly outweighs the potential risk to the foetus).
Breast-feeding
Pregabalin is excreted into human milk. The effect of pregabalin on newborns/infants is unknown. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue pregabalin therapy taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman.
Fertility
There are no clinical data on the effects of pregabalin on female fertility. In a clinical trial to assess the effect of pregabalin on sperm motility, healthy male subjects were exposed to pregabalin at a dose of 600 mg/day. After 3 months of treatment, there were no effects on sperm motility. A fertility study in female rats has shown adverse reproductive effects. Fertility studies in male rats have shown adverse reproductive and developmental effects. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Nortriptyline has moderate influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Nortriptyline may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of hazardous tasks, such as operating machinery or driving a car; therefore, the patient should be warned accordingly.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Mecobalamin
Adverse reactions were reported in 13 of 2,872 patients (0.45 %). (At the end of the re-examination period).
Clinically significant adverse reactions (incidence unknown).
Anaphylactoid reaction
Anaphylactoid reaction such as decrease in blood pressure or dyspnea, may occur. Patients should be carefully observed. In the event of such symptoms, treatment should be discontinued immediately and appropriate measures taken.
Pregabalin
The pregabalin clinical programme involved over 8900 patients exposed to pregabalin, of whom over 5600 were in double-blind placebo-controlled trials. The most commonly reported adverse reactions were dizziness and somnolence. Adverse reactions were usually mild to moderate in intensity. In all controlled studies, the discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions was 12% for patients receiving pregabalin and 5% for patients receiving placebo. The most common adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation from pregabalin treatment groups were dizziness and somnolence.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com Website : http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
No data are available about overdosage for Pregabalin (PR) 75 mg + Mecobalamin 1500 mcg +Nortriptyline10mg FilmCoatedBilayered tablet in humans.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action / Pharmacodynamic properties
Mecobalamin
- Mecobalamin is a Neurotropic and acts as a growth promoter for nerve cells, a property which helps to regenerate Central and Peripheral nervous tissue damaged in disorder such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
- Mecobalamin acts as a methyl donor for the synthesis of Lecithin, a major component of the Myelin sheath.
- Mecobalamin facilitates methylation of t-RNA which play a fundamental role in protein
synthesis and stimulates methionine synthesis and helps to restore normal levels of RNA in nerve cells.
- Mecobalamin acts as a co-factor in the enzyme methionine synthase which regenerates methionine thus generating an increased supply of S-Adenosyl Methionine (SAMe) and SAMe protects from Neurotoxicity.
- Mecobalamin normalizes Nerve cell conduction by healing the damaged nerve cells and restores delayed synaptic transmission and diminished neurotransmitters to normal.
- Mecobalamin improves the excitability of the nerve fibres and thus improves the neurotransmission.
Pregabalin
The active substance, pregabalin, is a gamma-aminobutyric acid analogue [(S)-3- (aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid]. Pregabalin binds to an auxiliary subunit (α2-δ protein) of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system.
Nortriptyline HCl
The mechanism of mood elevation by tricyclic antidepressants is at present unknown. Nortriptyline HCl is not a monoamine oxidase inhibitor. It inhibits the activity of such diverse agents as histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and acetylcholine. It increases the pressor effect of norepinephrine but blocks the pressor response of phenethylamine. Studies suggest that nortriptyline HCl interferes with the transport, release, and storage of catecholamines. Operant conditioning techniques in rats and pigeons suggest that nortriptyline HCL has a combination of stimulant and depressant properties.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Pregabalin
Absorption
Pregabalin is rapidly absorbed when administered in the fasted state, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 1 hour following both single and multiple dose administration. Pregabalin oral bioavailability is estimated to be ≥ 90% and is independent of dose. Following repeated administration, steady state is achieved within 24 to 48 hours. The rate of pregabalin absorption is decreased when given with food resulting in a decrease in Cmax by approximately 25-30% and a delay in tmax to approximately 2.5 hours. However, administration of pregabalin with food has no clinically significant effect on the extent of pregabalin absorption.
Distribution
In preclinical studies, pregabalin has been shown to cross the blood brain barrier in mice, rats, and monkeys. Pregabalin has been shown to cross the placenta in rats and is present in the milk of lactating rats. In humans, the apparent volume of distribution of pregabalin following oral administration is approximately 0.56 l/kg. Pregabalin is not bound to plasma proteins.
Biotransformation
Pregabalin undergoes negligible metabolism in humans. Following a dose of radiolabelled pregabalin, approximately 98% of the radioactivity recovered in the urine was unchanged pregabalin. The N-methylated derivative of pregabalin, the major metabolite of pregabalin found in urine, accounted for 0.9% of the dose. In preclinical studies, there was no indication of racemisation of pregabalin S-enantiomer to the R-enantiomer.
Elimination
Pregabalin is eliminated from the systemic circulation primarily by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Pregabalin mean elimination half-life is 6.3 hours. Pregabalin plasma clearance and renal clearance are directly proportional to creatinine clearance. Dose adjustment in patients with reduced renal function or undergoing haemodialysis is necessary.
Nortriptyline HCl
Nortriptyline is widely distributed throughout the body and is extensively bound to plasma and tissue protein. Plasma concentrations of Nortriptyline may vary widely between individuals and no simple correlation with therapeutic response has been established.
Mecobalamin
Absorbed vitamin B12 is transported via specific B12 binding proteins, transcobalamin I and II to the various tissues. The liver is the main organ for vitamin B12 storage. Gastrointestinal absorption of vitamin B12 depends on the presence of sufficient intrinsic factor and calcium ions. Intrinsic factor deficiency causes pernicious anaemia, which may be associated with subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord. Vitamin B12 is bound to intrinsic factor during transit through the stomach; separation occurs in the terminal ileum in the presence of calcium, and vitamin B12 enters the mucosal cell for absorption. It is then transported by the transcobalamin binding proteins. A small amount (approximately 1% of the total amount ingested) is absorbed by simple diffusion, but this mechanism is adequate only with very large doses.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
No known animal toxicology data
7.0 Description
Pregabalin is a medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and generalized anxiety disorder. Its use for epilepsy is as an add-on therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization in adults. Some off-label uses of pregabalin include restless leg syndrome, prevention of migraines, anxiety disorders, and alcohol withdrawal. When used before surgery it does not appear to affect pain after surgery but may decrease the use of opioids.
Mecobalamin, is a cobalamin, a form of vitamin B12. It differs from cyanocobalamin in that the cyano at the cobalt is replaced with a methyl group. Mecobalamin features an octahedral cobalt(III) centre and can be obtained as bright red crystals. From the perspective of coordination chemistry, Mecobalamin is notable as a rare example of a compound that contains metal-alkyl bonds. Nickel-methyl intermediates have been proposed for the final step of methanogenesis. Mecobalamin is equivalent physiologically to vitamin B12, and can be used to prevent or treat pathology arising from a lack of vitamin B12 intake (vitamin B12 deficiency). Mecobalamin is also used in the treatment of peripheral neuropathy, diabetic neuropathy, and as a preliminary treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mecobalamin that is ingested is not used directly as a cofactor, but is first converted by MMACHC into cob(II)alamin. Cob(II)alamin is then later converted into the other 2 forms, adenosylcobalamin and Mecobalamin for use as cofactors. That is, Mecobalamin is first dealkylated and then regenerated.
Nortriptyline, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) used to treat clinical depression. Another licensed use for it is in the treatment of childhood bedwetting. Off-label uses include chronic pain and migraine and labile affect in some neurological disorders. Chemically, it is a
secondary amine dibenzocycloheptene and pharmacologically it is classed as a secondgeneration TCA. Nortriptyline has less anticholinergic (like dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, etc.), antihistamine (like sedation and possibly weight gain), antiadrenergic (like orthostatic hypotension), and cardiotoxic (heart-toxic, namely the capacity of these drugs to interfere with normal heart rhythm) effects than the older first-generation TCAs. Nortriptyline is the major active metabolite of amitriptyline, a first-generation TCA. It is the N-desmethyl metabolite of amitriptyline. Like amitriptyline it works by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, thereby enhancing synaptic signalling via these neurotransmitters. It preferentially inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine over serotonin, which is the opposite to amitriptyline.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack
8.3 Packaging information
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C, protected from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Details of manufacturer
Do not take this medicine
if you are allergic to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
Warnings and precautions
- Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine:
- Some patients taking Upnuron have reported symptoms suggesting an allergic reaction. These symptoms include swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat, as well as diffuse skin rash. Should you experience any of these reactions, you should contact your physician immediately.
- Upnuron has been associated with dizziness and somnolence, which could increase the occurrence of accidental injury (fall) in elderly patients. Therefore, you should be careful until you are used to any effect the medicine might have.
- Upnuron may cause blurring or loss of vision, or other changes in eyesight, many of which are temporary. You should immediately tell your doctor if you experience any changes in your vision.
- Some patients with diabetes who gain weight while taking Upnuron may need an alteration in their diabetic medicines.
- Certain side effects may be more common, such as sleepiness, because patients with spinal cord injury may be taking other medicines to treat, for example, pain or spasticity, that have similar side effects to Upnuron and the severity of these effects may be increased when taken together.
- There have been reports of heart failure in some patients when taking Upnuron; these patients were mostly elderly with cardiovascular conditions.
Before taking this medicine you should tell your doctor if you have a history of heart disease.
- There have been reports of kidney failure in some patients when taking Upnuron. If while taking Upnuron you notice decreased urination, you should tell your doctor as stopping the medicine may improve this.
- A small number of people being treated with anti-epileptics such as Upnuron have had thoughts of harming or killing themselves. If at any time you have these thoughts, immediately contact your doctor.
- When Upnuron is taken with other medicines that may cause constipation (such as some types of pain medicines) it is possible that gastrointestinal problems may occur (e.g. constipation, blocked or paralysed bowel). Tell your doctor if you experience constipation, especially if you are prone to this problem.
- Before taking this medicine you should tell your doctor if you have a history of alcoholism or any drug abuse or dependence. Do not take more medicine than prescribed.
- There have been reports of convulsions when taking Upnuron or shortly after stopping Upnuron. If you experience a convulsion, contact your doctor immediately.
- There have been reports of reduction in brain function (encephalopathy) in some patients taking Upnuron when they have other conditions. Tell your doctor if you have a history of any serious medical conditions, including liver or kidney disease.
- There have been reports of breathing difficulties. If you have nervous system disorders, respiratory disorders, renal impairment, or you are older than 65, your doctor may prescribe you a different dosing regimen. Contact your doctor if you experience trouble breathing or shallow breaths.
- Serious skin rashes including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported in association with Upnuron. Stop using Upnuron and seek medical attention immediately if you notice any of the symptoms related to these serious skin reactions.
12.0 Date of revision
14 October 2022

About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child starts taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as your child’s.
- If your child gets any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet?
- What Upnuron™ is and what it is used for?
- What you need to know before you take Upnuron™?
- How to take Upnuron™?
- Possible side effects
- How to store Upnuron™?
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Upnuron™ is and what it is used for?
Upnuron™ tablet is a fixed dosed tablet of Pregabalin 75 mg, Methylcobalamin (Vitamin B12) 1500 mcg and Nortriptyline 10mg.
Pregabalin is an anti-convulsant medication used to treat neuropathic pain (pain caused by nerve damage). Pregabalin helps treat neuropathic pain by calming down overactive nerves in the brain and spinal cord. It reduces the release of certain chemicals that transmit pain signals, which helps to relieve pain and discomfort caused by nerve damage or other conditions.
Methylcobalamin, a form of vitamin B12, is used to help with nerve problems caused by diabetes. It supports nerve health, may help repair damaged nerves, and can reduce pain and other symptoms like tingling or numbness.
Nortriptyline is an antidepressant medication found to be effective in relieving neuropathic pain. It works by affecting certain chemicals in the brain and spine that are involved in transmitting pain signals. This can reduce feelings of burning, shooting pain, and tingling often experienced in conditions like diabetic neuropathy or other nerve-related issues.
Upnuron™ tablet is used for the treatment of patient with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain with coexistent Vitamin B12 Deficiency.
2. What you need to know before you take Upnuron™ Tablet?
Do not take Upnuron™ Tablet:
- If you are allergic to pregabalin, methylcobalamin, Nortriptyline or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have had a recent heart attack or heartbeat disorder
- if you have severe liver disease
- if you suffer from mania (abnormally raised mood)
- if you are breast-feeding
- if the child is under 6 years of age
- if you are taking, or have taken in the last two weeks, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (another type of antidepressant)
- if you are taking adrenaline-like drugs including ephedrine, isoprenaline, noradrenaline, phenylephrine and phenylpropanolamine. These drugs are often contained in cough and cold remedies
Warnings and Precautions:
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Upnuron™ tablet
- if you feel suicidal or aggressive - tell your doctor
- if you are agitated, overactive, or suffer from schizophrenia
- if you have heart disease
- if you have a cardiac condition called Brugada syndrome
- if you have a thyroid condition
- if you have a history of epilepsy
- if you have high pressure in the eyes (glaucoma)
- if you have an enlarged prostate
- if you are going to have electroconvulsive therapy (electric shock)
- if you are going to receive an anaesthetic, e.g. for an operation – tell your doctor
- if you have had an allergic reaction to another tricyclic antidepressant in the past
- if you are pregnant, think you might be pregnant or planning to become pregnant or breast-feeding
- Some patients taking Pregabalin have reported symptoms suggesting an allergic reaction. These symptoms include swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat, as well as diffuse skin rash. Should you experience any of these reactions, you should contact your physician immediately.
- Pregabalin has been associated with dizziness and somnolence, which could increase the occurrence of accidental injury (fall) in elderly patients. Therefore, you should be careful until you are used to any effect the medicine might have.
- Pregabalin may cause blurring or loss of vision, or other changes in eyesight, many of which are temporary.
- Some patients with diabetes who gain weight while taking Pregabalin may need an alteration in their diabetic medicines
- Taking Upnuron™ with medications that cause constipation may lead to gastrointestinal problems. Inform your doctor if you experience constipation, especially if you are prone to it.
- Before starting Upnuron™, inform your doctor if you have a history of alcoholism, drug abuse, or dependence. Take the prescribed dose and avoid taking more than directed.
- Serious skin rashes, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported with Upnuron™. Stop using Upnuron™ and seek medical attention immediately if you notice symptoms related to these serious skin reactions
Dependence
Some people may become dependent on Upnuron™ (a need to keep taking the medicine). They may have withdrawal effects when they stop using Upnuron™ (see section 3, “How to take Upnuron™” and “If you stop taking Upnuron™”). If you have concerns that you may become dependent on Upnuron™, it is important that you consult your doctor.
If you notice any of the following signs whilst taking Upnuron™, it could be a sign that you have become dependent:
- You need to take the medicine for longer than advised by your prescriber
- You feel you need to take more than the recommended dose
- You are using the medicine for reasons other than prescribed
- You have made repeated, unsuccessful attempts to quit or control the use of the medicine
- When you stop taking the medicine you feel unwell, and you feel better once taking the medicine again
If you notice any of these, speak to your doctor to discuss the best treatment pathway for you, including when it is appropriate to stop and how to do this safely.
Children and adolescents
Children and adolescents The safety and efficacy in children and adolescents (under 18 years of age) has not been established and therefore, Upnuron™ should not be used in this age group.
Other medicines and Upnuron™ tablet
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. The following medicines may interact with your Nortriptyline tablets
Mecobalamin
No known drug interaction.
Pregabalin
When taken with certain other medicines which have sedative effects (including opioids), Pregabalin may potentiate these effects, and could lead to respiratory failure, coma and death. The degree of dizziness, sleepiness and decreased concentration may be increased if Pregabalin is taken together with medicines containing:
- Oxycodone – (used as a pain-killer)
- Lorazepam – (used for treating anxiety)
- Alcohol
- Pregabalin may be taken with oral contraceptives
Nortriptyline
- guanethidine, debrisoquine, bethanidine, clonidine (used to treat high blood pressure)
- barbiturates (used for anxiety or to make you feel sleepy)
- alcohol (you should not drink alcohol)
- fluoxetine (another antidepressant)
- cimetidine (for heartburn and ulcers)
- phenothiazines (for mental illness)
- carbamazepine (for epilepsy)
- propafenone, flecainide, encainide, quinidine (for heartbeat disorders)
- valproic acid (medicine used for the treatment of epilepsy and bipolar disorder)
- buprenorphine/opioids: These medicines may interact with Nortriptyline tablets and you may experience symptoms such as involuntary, rhythmic contractions of muscles, including the muscles that control movement of the eye, agitation, hallucinations, coma, excessive sweating, tremor, exaggeration of reflexes, increased muscle tension, body temperature above 38°C. Contact your doctor when experiencing such symptoms.
It may still be all right for you to be given Upnuron™ tablets. Your doctor will be able to decide what is suitable for you.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Pregabalin should not be taken during pregnancy or when breast-feeding, unless you are told otherwise by your doctor. Pregabalin use during the first 3 months of pregnancy may cause birth defects in the unborn child that require medical treatment.
Effective contraception must be used by women of childbearing potential. If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Upnuron™ tablets may affect alertness. Use caution when driving or operating heavy machinery until you’re aware of how this drug affects you. If you feel Upnuron™ tablets affect your ability to drive or use machines, tell your doctor immediately.
3. How to take Upnuron™ Tablet.
Always take Upnuron™ tablet exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Dosage in Adults:
General recommended dosage is one tablet daily or as directed by the Physician
Upnuron™ tablet is for oral use only
Children and adolescents The safety and efficacy in children and adolescents (under 18 years of age) has not been established and therefore, Upnuron™ should not be used in this age group
If you take more Upnuron™ tablet
than you should Go to the nearest casualty department or contact your doctor immediately. Take the tablet carton with you.
If you forget to take Upnuron™ tablet If you miss a dose, take one as soon as you can. If you have missed several doses, tell your doctor. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking Upnuron™ tablets
Do not stop taking the tablets or reduce the dose without telling your doctor first. If you suddenly stop taking the tablets you may feel sick (nausea), have a headache or feel generally unwell.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist
4. Possible side-effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people
Dizziness, drowsiness, headache
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Increased appetite
- Dry mouth, constipation, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhoea, nausea, swollen abdomen
- Disturbance in attention, clumsiness, memory impairment, loss of memory, tremor, difficulty with speaking, tingling feeling, numbness, sedation, lethargy, insomnia, fatigue, feeling abnormal.
- Feeling drunk, abnormal style of walking
- Weight gain
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- Change in perception of self, restlessness, depression, agitation, mood swings, difficulty finding words, hallucinations, abnormal dreams, panic attack, apathy, aggression, elevated mood, mental impairment, difficulty with thinking
- Dry eyes, eye swelling, eye pain, weak eyes, watery eyes, eye irritation.
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- Allergic reactions which may include difficulty breathing, inflammation of the eyes (keratitis) and serious skin reactions characterized by reddish non-elevated, target-like or circular patches on the trunk, often with central blisters, skin peeling, ulcers of mouth, throat, nose, genitals and eyes. These serious skin rashes can be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis)
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
You can also report side effects directly:
Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page. Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Upnuron™?
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children
Store in a dry place below 30°C.
Protect from light & moisture.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Pack size: Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets
Each film coated bilayered tablet contains:
Pregabalin IP (Prolonged Release) 75 mg
Methylcobalamin IP 1500 mcg
Nortriptyline Hydrochloride IP equivalent to Nortriptyline 10 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Sunset Yellow Lake
(In Methylcobalamin & Nortriptyline layer)
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Zuventus Heathcare Ltd.
Zuventus House, Plot Y2, CTS No: 358/A2,
Near Nahur Railway Station,
Nahur (West), Mumbai 400 078.
This leaflet was last revised in June 2024.