Zutig 50 Injection
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Generic name
Tigecycline Injection IP 50 mg
2.0 Quantitative and qualitative composition
Each vial contains :
Tigecycline IP 50 mg
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Injection 50 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Zutig is indicated in adults and in children from the age of eight years for the treatment of the following infections :
- Skin & skin structure infection
- Intra abdominal infection
Zutig should be used only in situations where other alternative antibiotics are not suitable.
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
4.2 Posology & method of administration
Adults
The recommended dose for adults is an initial dose of 100 mg followed by 50 mg every 12 hours for 5 to 14 days. The duration of therapy should be guided by the severity, site of the infection, and the patient's clinical response.
Children and adolescents (8 to 17 years of age)
Tigecycline is only to be used to treat patients aged 8 years and older after consultation with a physician with appropriate experience in the management of infectious diseases.
Children aged 8 to <12 years: 1.2 mg/kg of tigecycline every 12 hours intravenously to a maximum dose of 50 mg every 12 hours for 5 to 14 days.
Adolescents aged 12 to <18 years : 50 mg of tigecycline every 12 hours for 5 to 14 days.
Elderly
No dosage adjustment is necessary in elderly patients.
Hepatic impairment
No dosage adjustment is warranted in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh A and Child Pugh B). In patients (including paediatrics) with severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh C), the dose of tigecycline should be reduced by 50%. Adult dose should be reduced to 25 mg every 12 hours following the 100 mg loading dose. Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh C) should be treated with caution and monitored for treatment response.
Renal impairment
No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with renal impairment or in patients undergoing haemodialysis.
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy of Zutig in children under 8 years of age have not been established. No data are available. Zutig should not be used in children aged under 8 years because of teeth discolouration.
Method of administration
Zutig 50 mg vial should be reconstituted with 5 ml of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection lP or 5% Dextrose lnjection lP or Lactated Ringers injection to achieve a concentration of 10 mg/ml of Tigecycline. The vial should be gently swirled until the drug dissolves. Immediately withdraw entire content of the reconstituted solution from the vial and add to a 100 ml l.V. bag for infusion (for a 100 mg dose, reconstitute two vials; for a 50 mg dose, reconstitute one vial). The maximum concentration of the l.V. bag should be 1mg/ml. The reconstituted solution should be yellow to orange in colour; if not, the solution should be discarded. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration (e.g., green or black) prior to administration. Zutig may be stored in the lV bag at room temperature for upto 6 hour, or refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36 to 46°F) for upto 48 hours. Zutig may be administered intravenously through a dedicated line or through a Y site. If the same intravenous line is used for sequential infusion of several drugs, the line should be thoroughly flushed before and after infusion of Zutig.
Compatibilities
Compatible intravenous solutions include 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection IP, 5% Dextrose injection IP, and Lactated Ringers injection. When administered through a Y-site, Zutig is compatible with the following drugs or diluents when used with either 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection IP or 5% Dextrose Injection IP, amikacin, dobutamine, dopamine HCl, gentamicin, haloperidol. Lactated Ringers, lidocaine HCl, metoclopramide, morphine, norepinephrine, piperacillin / tazobactam (EDTA formulation), potassium chloride, propofol, ranitidine HCL, theophylline and tobramycin.
4.3 Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in the formulation.
• Patients hypersensitive to tetracycline class antibiotics may be hypersensitive to tigecycline.
4.4 Warning & precautions
In clinical studies in complicated skin and soft tissue infections (cSSTI), complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI), diabetic foot infections, nosocomial pneumonia and studies in resistant pathogens, a numerically higher mortality rate among tigecycline treated patients has been observed as compared to the comparator treatment. The causes of these findings remain unknown, but poorer efficacy and safety than the study comparators cannot be ruled out.
Superinfection
In clinical trials in cIAI patients, impaired healing of the surgical wound has been associated with superinfection. A patient developing impaired healing should be monitored for the detection of superinfection. Patients who develop superinfections, in particular nosocomial pneumonia, appear to be associated with poorer outcomes. Patients should be closely monitored for the development of superinfection. If a focus of infection other than cSSTI or cIAI is identified after initiation of tigecycline therapy consideration should be given to instituting alternative antibacterial therapy that has been demonstrated to be efficacious in the treatment of the specific type of infection(s) present.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis/anaphylactoid reactions, potentially life-threatening, have been reported with tigecycline.
Hepatic failure
Cases of liver injury with a predominantly cholestatic pattern have been reported in patients receiving tigecycline treatment, including some cases of hepatic failure with a fatal outcome. Although hepatic failure may occur in patients treated with tigecycline due to the underlying conditions or concomitant medicinal products, a possible contribution of tigecycline should be considered.
Tetracycline class antibiotics
Glycylcycline class antibiotics are structurally similar to tetracycline class antibiotics. Tigecycline may have adverse reactions similar to tetracycline class antibiotics. Such reactions may include photosensitivity, pseudotumor cerebri, pancreatitis, and anti-anabolic action which has led to increased BUN, azotaemia, acidosis, and hyperphosphataemia.
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, which can be serious, has occurred (frequency: uncommon) in association with tigecycline treatment. The diagnosis of acute pancreatitis should be considered in patients taking tigecycline who develop clinical symptoms, signs, or laboratory abnormalities suggestive of acute pancreatitis. Most of the reported cases developed after at least one week of treatment. Cases have been reported in patients without known risk factors for pancreatitis. Patients usually improve after tigecycline discontinuation. Consideration should be given to the cessation of the treatment with tigecycline in cases suspected of having developed pancreatitis.
Coagulopathy
Tigecycline may prolong both prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). Additionally, hypofibrinogenaemia has been reported with the use of tigecycline. Therefore, blood coagulation parameters such as PT or other suitable anticoagulation test, including blood fibrinogen, should be monitored prior to treatment initiation with tigecycline and regularly while on treatment. Special care is recommended in seriously ill patients and in patients also using anticoagulants.
Underlying diseases
Experience in the use of tigecycline for treatment of infections in patients with severe underlying diseases is limited. Consideration should be given to the use of combination antibacterial therapy whenever tigecycline is to be administered to severely ill patients with cIAI secondary to clinically apparent intestinal perforation or patients with incipient sepsis or septic shock. The effect of cholestasis in the pharmacokinetics of tigecycline has not been properly established. Biliary excretion accounts for approximately 50 % of the total tigecycline excretion. Therefore, patients presenting with cholestasis should be closely monitored. Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents and may range in severity from mild to life threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhoea during or subsequent to the administration of any antibacterial agent. The use of tigecycline may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms, including fungi. Patients should be carefully monitored during therapy. Results of studies in rats with tigecycline have shown bone discolouration. Tigecycline may be associated with permanent tooth discolouration in humans if used during tooth development.
Paediatric population
Clinical experience in the use of tigecycline for the treatment of infections in paediatric patients aged 8 years and older is very limited. Consequently, use in children should be restricted to those clinical situations where no alternative antibacterial therapy is available. Nausea and vomiting are very common adverse reactions in children and adolescents. Attention should be paid to possible dehydration. Tigecycline should be preferably administered over a 60-minute length of infusion in paediatric patients. Abdominal pain is commonly reported in children as it is in adults. Abdominal pain may be indicative of pancreatitis. If pancreatitis develops, treatment with tigecycline should be discontinued. Liver function tests, coagulation parameters, haematology parameters, amylase and lipase should be monitored prior to treatment initiation with tigecycline and regularly while on treatment. Tigecycline Injection should not be used in children under 8 years of age due to the lack of safety and efficacy data in this age group and because tigecycline may be associated with permanent teeth discolouration.
4.5 Drug interactions
Interaction studies have only been performed in adults. Concomitant administration of tigecycline and warfarin (25 mg single-dose) to healthy subjects resulted in a decrease in clearance of R-warfarin and S-warfarin by 40 % and 23 %, and an increase in AUC by 68 % and 29 %, respectively. The mechanism of this interaction is still not elucidated. Available data does not suggest that this interaction may result in significant INR changes. However, since tigecycline may prolong both prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), the relevant coagulation tests should be closely monitored when tigecycline is co-administered with anticoagulants. Warfarin did not affect the pharmacokinetic profile of tigecycline.
Tigecycline is not extensively metabolised. Therefore, clearance of tigecycline is not expected to be affected by active substances that inhibit or induce the activity of the CYP450 isoforms. In vitro, tigecycline is neither a competitive inhibitor nor an irreversible inhibitor of CYP450 enzymes.
Tigecycline in recommended dosage did not affect the rate or extent of absorption, or clearance of digoxin (0.5 mg followed by 0.25 mg daily) when administered in healthy adults. Digoxin did not affect the pharmacokinetic profile of tigecycline. Therefore, no dosage adjustment is necessary when tigecycline is administered with digoxin. In in vitro studies, no antagonism has been observed between tigecycline and other commonly used antibiotic classes. Concurrent use of antibiotics with oral contraceptives may render oral contraceptives less effective. Concomitant use of tigecycline and calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus or cyclosporine may lead to an increase in serum trough concentrations of the calcineurin inhibitors. Therefore, serum concentrations of the calcineurin inhibitor should be monitored during treatment with tigecycline to avoid drug toxicity
Based on an in vitro study tigecycline is a P-gp substrate. Co-administration of P-gp inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole or cyclosporine) or P-gp inducers (e.g., rifampicin) could affect the pharmacokinetics of tigecycline.
4.6 Special populations
Pregnancy
There are no or limited amount of data from the use of tigecycline in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity. The potential risk for humans is unknown. As it is known for tetracycline class antibiotics, tigecycline may also induce permanent dental defects (discolouration and enamel defects) and a delay in ossification processes in foetuses, exposed in utero during the last half of gestation, and in children under eight years of age due to the enrichment in tissues with a high calcium turnover and formation of calcium chelate complexes. Tigecycline should not be used during pregnancy unless the clinical condition of the woman requires treatment with tigecycline.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown whether tigecycline / metabolites are excreted in human milk. Available pharmacodynamic / toxicological data in animals have shown excretion of tigecycline / metabolites in milk. A risk to the newborns / infants cannot be excluded. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue / abstain from tigecycline therapy taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman.
Fertility
The effects of tigecycline on fertility in humans have not been studied. Nonclinical studies conducted with tigecycline in rats do not indicate harmful effects with respect to fertility or reproductive performance. In female rats, there were no compound-related effects on ovaries or oestrus cycles at exposures up to 4.7 times the human daily dose based on AUC.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Dizziness may occur and this may have an effect on driving and use of machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
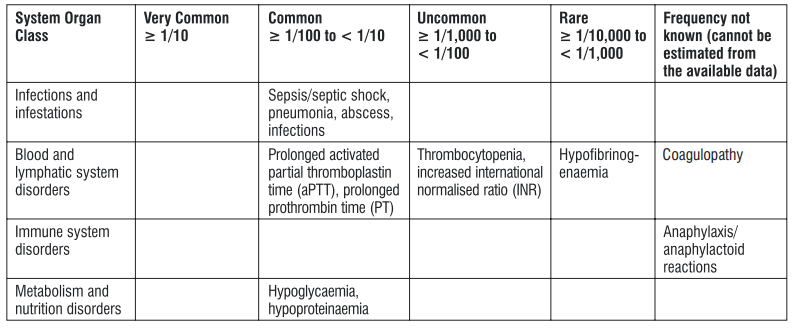
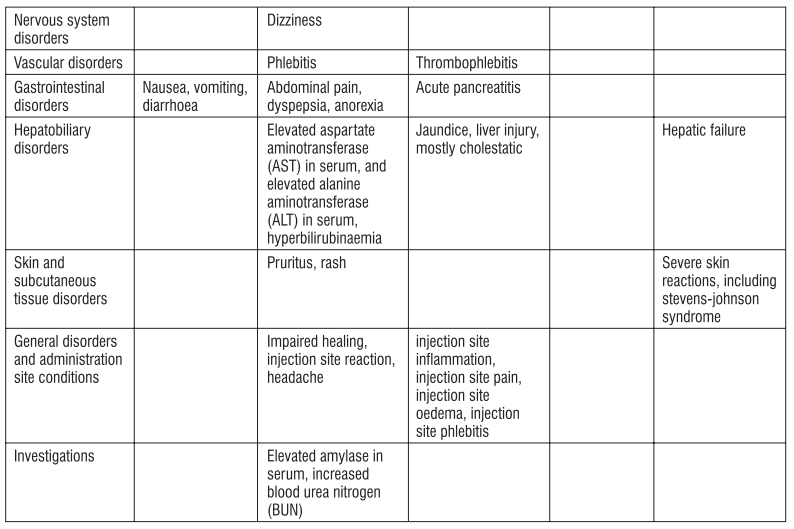
In clinical trials, the most common medicinal product-related treatment emergent adverse reactions were reversible nausea and vomiting, which usually occurred early (on treatment days 1-2) and were generally mild or moderate in severity. Adverse reactions reported with tigecycline, including clinical trials and post-marketing experience, are tabulated below. Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
No specific information is available on the treatment of overdosage. Intravenous administration of tigecycline at a single dose of 300 mg over 60 minutes in healthy volunteers resulted in an increased incidence of nausea and vomiting. Tigecycline is not removed in significant quantities by haemodialysis.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Tigecycline, a glycylcycline antibiotic, inhibits protein translation in bacteria by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit and blocking entry of amino-acyl tRNA molecules into the A site of the ribosome. This prevents incorporation of amino acid residues into elongating peptide chains. In general, tigecycline is considered bacteriostatic. At 4 times the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), a 2-log reduction in colony counts was observed with tigecycline against Enterococcus spp., Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Mechanism of resistance
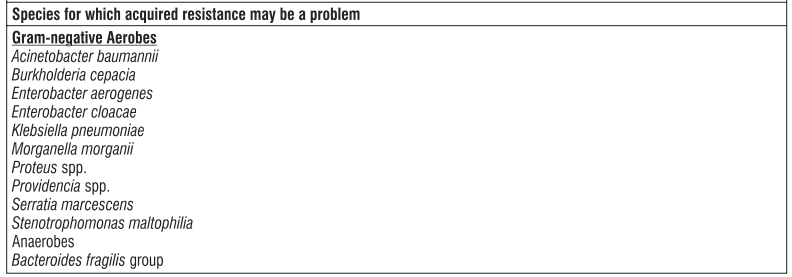
Tigecycline is able to overcome the two major tetracycline resistance mechanisms, ribosomal protection and efflux. Cross-resistance between tigecycline and minocycline-resistant isolates among the Enterobacteriaceae due to multi-drug resistance (MDR) efflux pumps has been shown. There is no target-based cross-resistance between tigecycline and most classes of antibiotics. Tigecycline is vulnerable to chromosomally-encoded multi-drug efflux pumps of Proteeae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pathogens of the family Proteeae (Proteus spp., Providencia spp., and Morganella spp.) are generally less susceptible to tigecycline than other members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Decreased susceptibility in both groups has been attributed to the overexpression of the non-specific AcrAB multi-drug efflux pump. Decreased susceptibility in Acinetobacter baumannii has been attributed to the overexpression of the AdeABC efflux pump.
Susceptibility
The prevalence of acquired resistance may vary geographically and with time for selected species, and local information on resistance is desirable, particularly when treating severe infections. As necessary, expert advice should be sought when the local prevalence of resistance is such that the utility of the agent in at least some types of infections is questionable.


5.3 Pharmacokinetic proper
Absorption
Tigecycline is administered intravenously and therefore has 100% bioavailability ties
Distribution
The in vitro plasma protein binding of tigecycline ranges from approximately 71 % to 89 % at concentrations observed in clinical studies (0.1 to 1.0 mcg/ml). Animal and human pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that tigecycline readily distributes to tissues. 14 In rats receiving single or multiple doses of C-tigecycline, radioactivity was well distributed to most tissues, with the highest overall exposure observed in bone marrow, salivary glands, thyroid gland, spleen, and kidney. In humans, the steady-state volume of distribution of tigecycline averaged 500 to 700 L (7 to 9 L/kg), indicating that tigecycline is extensively distributed beyond the plasma volume and concentrates into tissues. No data are available on whether tigecycline can cross the blood-brain barrier in humans. In clinical pharmacology studies using the therapeutic dosage regimen of 100 mg followed by 50 mg q12h, serum tigecycline steadystate Cmax was 866±233 ng/ml for 30-minute infusions and 634±97 ng/ml for 60-minute infusions. The steady-state AUC0-12h was 2349±850 ng•h/ml.
Biotransformation
On average, it is estimated that less than 20 % of tigecycline is metabolised before excretion. In healthy male volunteers, following the 14 14 administration of C-tigecycline, unchanged tigecycline was the primary C-labelled material recovered in urine and faeces, but a glucuronide, an N-acetyl metabolite and a tigecycline epimer were also present. In vitro studies in human liver microsomes indicate that tigecycline does not inhibit metabolism mediated by any of the following 6 cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms: 1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4 by competitive inhibition. In addition, tigecycline did not show NADPH-dependency in the inhibition of CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A, suggesting the absence of mechanism-based inhibition of these CYP enzymes.
Elimination
The recovery of the total radioactivity in faeces and urine following administration of C-tigecycline indicates that 59 % of the dose is eliminated by biliary/faecal excretion, and 33 % is excreted in urine. Overall, the primary route of elimination for tigecycline is biliary excretion of unchanged tigecycline. Glucuronidation and renal excretion of unchanged tigecycline are secondary routes. The total clearance of tigecycline is 24 L/h after intravenous infusion. Renal clearance is approximately 13 % of total clearance. Tigecycline shows a polyexponential elimination from serum with a mean terminal elimination half-life after multiple doses of 42 hours although high interindividual variability exists.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
In repeated dose toxicity studies in rats and dogs, lymphoid depletion / atrophy of lymph nodes, spleen and thymus, decreased erythrocytes, reticulocytes, leukocytes, and platelets, in association with bone marrow hypocellularity, and adverse renal and gastrointestinal effects have been seen with tigecycline at exposures of 8 and 10 times the human daily dose based on AUC in rats and dogs, respectively. These alterations were shown to be reversible after two weeks of dosing. Bone discolouring was observed in rats which was not reversible after two weeks of dosing. Results of animal studies indicate that tigecycline crosses the placenta and is found in foetal tissues. In reproduction toxicity studies, decreased foetal weights in rats and rabbits (with associated delays in ossification) have been observed with tigecycline. Tigecycline was not teratogenic in the rat or rabbit. Tigecycline did not affect mating or fertility in rats at exposures up to 4.7 times the human daily dose based on AUC. In female rats, there were no compound-related effects on ovaries or oestrus cycles at exposures up to 4.7 times the human daily dose based on AUC. R 14 esults from animal studies using C-labelled tigecycline indicate that tigecycline is excreted readily via the milk of lactating rats. Consistent with the limited oral bioavailability of tigecycline, there is little or no systemic exposure to tigecycline in the nursing pups as a result of exposure via maternal milk. Lifetime studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of tigecycline have not been performed, but short-term genotoxicity studies of tigecycline were negative. Bolus intravenous administration of tigecycline has been associated with a histamine response in animal studies. These effects were observed at exposures of 14 and 3 times the human daily dose based on the AUC in rats and dogs respectively. No evidence of photosensitivity was observed in rats following administration of tigecycline.
7.0 Description
Tigecycline for injection, IP is a tetracycline class antibacterial for intravenous infusion. The chemical name of tigecycline is (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-9-[2-(tert-butylamino)acetamido]-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12atetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenecarboxamide
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
The following drugs should not be administered simultaneously through the same Y-site as Zutig : amphotericin B, amphotericin B lipid complex, diazepam, esomeprazole and omeprazole.
8.2 Shelf life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
A vial of 50 mg.
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store protected from light & moisture, at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Advise patients, their families, or caregivers that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs. Sometimes, frequent watery or bloody diarrhea may occur and may be a sign of a more serious intestinal infection. If severe watery or bloody diarrhea develops, tell them to contact his or her healthcare provider. Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including tigecycline should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When tigecycline is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by tigecycline or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for you or your child.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet:
- What Zutig is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you receive Zutig
- How Zutig is given
- Possible side effects
- How to store Zutig
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Zutig is and what it is used for
Zutig is an antibiotic of the glycylcycline group that works by stopping the growth of bacteria that cause infections.
Your doctor has prescribed Zutig because you or your child at least 8 years old has one of the following types of serious infections:
- Complicated infection of the skin and soft tissues (the tissue below the skin), excluding diabetic foot infections.
- Complicated infection in the abdomen.
Zutig is only used when your doctor thinks other antibiotics are not suitable.
2. What you need to know before you receive Zutig
Do not use Zutig
- If you are allergic to tigecycline, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine. If you are allergic to tetracycline class antibiotics (e.g., minocycline, doxycycline, etc.), you may be allergic to tigecycline.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or nurse before receiving Zutig:
If you have poor or slow wound healing.
If you are suffering from diarrhoea before you are given Zutig.
If you develop diarrhoea during or after your treatment, tell your doctor at once. Do not take any diarrhoea medicine without first checking with your doctor.
If you have or previously had any side effects due to antibiotics belonging to the tetracycline class (e.g., skin sensitization to sun light, staining on developing teeth, pancreas inflammation, and alteration of certain laboratory values aimed at measuring how well your blood clots).
If you have, or previously had liver problems. Depending on the condition of your liver, your doctor may reduce the dose to avoid potential side effects. If you have blockage of the bile ducts (cholestasis). If you suffer from a bleeding disorder or are in treatment with anticoagulant drugs, as this medicine can interfere with blood coagulation.
During treatment with Zutig:
Tell your doctor immediately if you develop symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Tell your doctor immediately if you develop severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. These may be symptoms of acute pancreatitis (inflamed pancreas which may result in severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting).
In certain serious infections, your doctor may consider to use Zutig in combination with other antibiotics.
Your doctor will monitor you closely for the development of any other bacterial infections. If you develop another bacterial infection, your doctor may prescribe a different antibiotic specific for the type of infection present.
Although antibiotics including Zutig fight certain bacteria, other bacteria and fungi may continue to grow. This is called overgrowth. Your doctor will monitor you closely for any potential infections and treat you if necessary.
Children
Zutig is not to be used in children less than 8 years of age due to the lack of data on safety and efficacy in this age group and because it may induce permanent dental defects such as staining on the developing teeth.
Other medicines and Zutig
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. Zutig may prolong certain tests that measure how well your blood is clotting. It is important that you tell your doctor if you are taking medicines to avoid an excess of blood clotting (named anticoagulants). If this were the case, your doctor will monitor you closely.
Zutig may interfere with the contraceptive pill (birth control pill). Talk to your doctor about the need for an additional method of contraception while receiving Zutig. Zutig may increase the effect of medicines used to suppress the immune system (such as tacrolimus or cyclosporine). It is important that you tell your doctor if you are taking these medicines so you can be closely monitored.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Zutig may cause foetal harm. If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before receiving Zutig. It is not known if Zutig passes into breast milk in humans. Ask your doctor for advice before breast-feeding your baby.
Driving and using machines
Zutig may cause side effects such as dizziness. This may impair your ability to drive or operate machinery.
3. How Zutig is given
Zutig will be given to you by a doctor or a nurse. The recommended dose in adults is 100 mg given initially, followed by 50 mg every 12 hours. This dose is given intravenously (directly into your blood stream) over a period of 30 to 60 minutes. The recommended dose in children aged 8 to < 12 years is 1.2 mg/kg given every 12 hours intravenously to a maximum dose of 50 mg every 12 hours The recommended dose in adolescents aged 12 to < 18 years is 50 mg given every 12 hours. A course of treatment usually lasts for 5 to 14 days. Your doctor will decide how long you should be treated.
If you receive more Zutig than you should
If you are concerned that you may have been given too much Zutig, talk to your doctor or nurse immediately.
If you miss a dose of Zutig
If you are concerned that you may have missed a dose, talk to your doctor or nurse immediately.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Pseudomembranous colitis may occur with most antibiotics including Zutig. This consists of severe, persistent or bloody diarrhoea associated with abdominal pain or fever, which can be a sign of serious bowel inflammation, which may occur during or after your treatment.
Very common side effects are (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea.
Common side effects are (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Abscess (collection of pus), infections
- Laboratory measurements of decreased ability to form blood clots
- Dizziness
- Vein irritations from the injection, including pain, inflammation, swelling and clotting
- Abdominal pain, dyspepsia (stomach ache and indigestion), anorexia (loss of appetite)
- Increases in liver enzymes, hyperbilirubinaemia (excess of bile pigment in the blood)
- Pruritus (itching), rash
- Poor or slow wound healing
- Headache
- Increase in amylase, which is an enzyme found in the salivary glands and pancreas, increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
- Pneumonia
- Low blood sugar
- Sepsis (severe infection in the body and blood stream)/septic shock (serious medical condition which can lead to multiple organ failure and death as a result of sepsis)
- Injection site reaction (pain, redness, inflammation)
- Low protein levels in the blood
Uncommon side effects are (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Acute pancreatitis (inflamed pancreas which may result in severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting)
- Jaundice (yellow coloration of the skin), inflammation of the liver
- Low platelet levels in the blood (which may lead to an increased bleeding tendency and bruising/haematoma)
- Rare side effects are (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- Low fibrinogen levels in the blood (a protein involved in blood clotting) Not known side effects are (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Anaphylaxis/anaphylactoid reactions (that may range from mild to severe, including a sudden, generalised allergic reaction that may lead to a life-threatening shock [e.g. difficulty in breathing, drop of blood pressure, fast pulse])
- Liver failure
- Skin rash, which may lead to severe blistering and peeling of the skin (Stevens-Johnson Syndrome)
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Zutig
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Store below 25°C.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the vial. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Storage after preparation
Once the powder has been made into a solution and diluted ready for use, it should be given to you immediately. Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Zutig contains
The active substance is tigecycline. Each vial contains 50 mg of tigecycline.
What Zutig looks like and contents of the pack
Zutig is supplied as a powder for solution for infusion in a vial. 50 mg / Vial
Single Dose Vial