C Tax Injection 1.0 gm
1.0 Generic name
Cefotaxime Sodium Injection IP 250 mg / 500 mg / 1 gm
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
C-Tax 250
Each vial contains:
Cefotaxime Sodium IP
equivalent to Cefotaxime 250 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
C-Tax 500
Each vial contains:
Cefotaxime Sodium IP
equivalent to Cefotaxime 500 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
C-Tax 1.0 g
Each vial contains:
Cefotaxime Sodium IP
equivalent to Cefotaxime 1.0 g
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Powder for solution for injection/infusion
250 mg / 500 mg / 1 gm
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1.Therapeutic indication
Indicated in the treatment of patients with serious infections.
1. Cefotaxime is indicated in the treatment of serious infections, either before the infecting organism has been identified or when caused by bacteria of established sensitivity, including
- osteomyelitis,
- septicaemia,
- bacterial endocarditis,
- meningitis,
- peritonitis
- and other serious bacterial infections suitable for parenteral antibiotic therapy.
2. Cefotaxime may be used for pre-operative prophylaxis in patients undergoing surgical procedures, that may be classified as contaminated or potentially so.
4.2.Posology and method of administration
Cefotaxime may be administered intravenously by bolus injection or by infusion, or by intramuscular injection. The dosage, route and frequency of administration should be determined by the severity of infection, the sensitivity of causative organisms and condition of the patient. Therapy may be initiated before the results of sensitivity tests are known.
Adults:
The recommended dosage for mild to moderate infections is 1g 12 hourly. However, dosage may be varied according to the severity of the infection, sensitivity of causative organisms and condition of the patient. Therapy may be initiated before the results of sensitivity tests are known.
In severe infections dosage may be increased up to 12g daily given in three or four divided doses. For infections caused by sensitive Pseudomonas species daily doses of greater than 6g will usually be required.
Children:
The usual dosage range is 100-150mg/kg/day in two to four divided doses. However, in very severe infection doses of up to 200mg/kg/day may be required.
Neonates: The recommended dosage is 50mg/kg/day in two to four divided doses. In severe infections 150-200mg/kg/day, in divided doses, have been given.
Dosage in renal impairment: Because of extra-renal elimination, it is only necessary to reduce the dosage of cefotaxime in severe renal failure (GFR <5ml/min = serum creatinine approximately 751 micromol/litre). After an initial loading dose of 1g, daily dose should be halved without change in the frequency of dosing, i.e. 1g twelve hourly becomes 0.5g twelve hourly, 1g eight hourly becomes 0.5g eight hourly, 2g eight hourly becomes 1g eight hourly etc. As in all other patients, dosage may require further adjustment according to the course of the infection and the general condition of the patient.
Dosage in hepatic impairment: No dosage adjustment is required.
Intravenous and Intramuscular Administration
Dissolve the contents in 3 ml (for 250 mg / 500 mg) or 5 ml (for 1 gm) of Sterile Water for Injections IP, provided with this pack. Use immediately after reconstitution. Any unused portion must be discarded. After reconstitution, do not use in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
Intravenous Administration (Injection or Infusion): For intermittent I.V. injections, the solution must be injected over a period of 3 to 5 minutes.
Intravenous Infusion: 1-2 gm cefotaxime are dissolved in 40-100 ml of infusion fluid. After 24 hours any unused solution should be discarded. The prepared infusion may be administered over 20-60 minutes. Cefotaxime and aminoglycosides should not be mixed in the same syringe or perfusion fluid.
Compatible Infusion Solutions:
- Sodium Chloride 0.9%
- Dextrose 5 and 10%
- Ringer-Lactate Solution
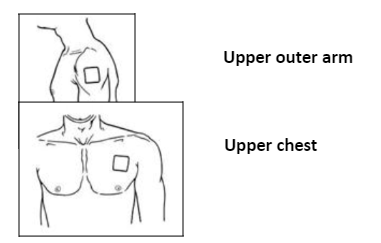
Intramuscular Administration: Cefotaxime should be injected well within the body of a relatively large muscle such as the upper outer quadrant of the buttock; aspiration is necessary to avoid inadvertent injection into a blood vessel.
4.3.Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins.
- In patients with a history of hypersensitivity to Cefotaxime and/or to any of the component listed in the formulation, a penicillin or to any other type of β-lactam drug.
- Allergic cross reactions can exist between penicillins and cephalosporins.
4.4.Special warnings and precautions for use
As with other antibiotics, the use of cefotaxime, especially if prolonged, may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms, such as Enterococcus spp, candida, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Repeated evaluation of the condition of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during treatment with cefotaxime, appropriate measures should be taken and specific anti-microbial therapy should be instituted if considered clinically necessary.
Anaphylactic reactions: Preliminary enquiry about hypersensitivity to penicillin and other β -Lactam antibiotics is necessary before prescribing cephalosporins since cross allergy occurs in 5– 10% of cases. The use of cefotaxime is strictly contra-indicated in subjects with a previous history of immediate-type hypersensitivity to cephalosporins. Since cross allergy exists between penicillins and cephalosporins, use of the latter should be undertaken with extreme caution in penicillin sensitive subjects. Serious, including fatal hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients receiving cefotaxime (see sections 4.3 and 4.8). If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, treatment must be stopped.
Severe skin reactions: Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) including acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), which can be life-threatening or fatal, have been reported post-marketing in association with cefotaxime treatment.
At the time of prescription patients should be advised of the signs and symptoms for skin reactions.
If signs and symptoms suggestive of these reactions appear, cefotaxime should be withdrawn immediately. If the patient has developed AGEP, SJS, TEN or DRESS with the use of cefotaxime, treatment with cefotaxime must not be restarted and should be permanently discontinued.
In children, the presentation of a rash can be mistaken for the underlying infection or an alternative infectious process, and physicians should consider the possibility of a reaction to cefotaxime in children that develop symptoms of rash and fever during therapy with cefotaxime.
Patients with renal insufficiency: The dosage should be modified according to the creatinine clearance calculated. Patients with severe renal dysfunction should be placed on the dosage schedule recommended under “Posology and Method of Administration”.
Caution should be exercised if cefotaxime is administered together with aminoglycosides, probenecid or other nephrotoxic drugs (see section 4.5). Renal function must be monitored in these patients, the elderly, and those with pre-existing renal impairment.
Haematological reactions: Leukopenia, neutropenia, and more rarely, agranulocytosis may develop during treatment with cefotaxime, particularly if given over long periods. For treatment courses lasting longer than 7-10 days, the blood white cell count should be monitored and treatment stopped in the event of neutropenia.
Some cases of eosinophilia and thrombocytopenia, rapidly reversible on stopping treatment, have been reported. Cases of haemolytic anaemia have also been reported (see section 4.8).
Sodium intake: The sodium content of cefotaxime (2.09mmol/g) should be taken into account when prescribing to patients requiring sodium restriction.
Clostridium difficile associated disease (e.g. pseudomembranous colitis): Cefotaxime may predispose patients to pseudomembranous colitis. Although any antibiotic may predispose to pseudomembranous colitis, the risk is higher with broad spectrum drugs, such as cephalosporins. This side effect, which may occur more frequently in patients receiving higher doses for prolonged periods, should be considered as potentially serious.
Diarrhoea, particularly if severe and/or persistent, occurring during treatment or in the initial weeks following treatment, may be symptomatic of Clostridium difficile associated disease (CDAD). CDAD may range in severity from mild to life threatening, the most severe form of which is pseudo-membranous colitis.
The diagnosis of this rare but possibly fatal condition can be confirmed by endoscopy and/or histology.
It is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhoea during or subsequent to the administration of cefotaxime.
If a diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis is suspected, cefotaxime should be stopped immediately and appropriate specific antibody therapy should be started without delay.
Clostridium difficile associated disease can be favoured by faecal stasis.
Medicinal products that inhibit peristalsis should not be given.
Neurotoxicity: High doses of beta-lactam antibiotics, including cefotaxime, particularly in patients with renal insufficiency, may result in encephalopathy (e.g. impairment of consciousness, abnormal movements and convulsions).
Patients should be advised to contact their doctor immediately prior to continuing treatment if such reactions occur.
Precautions for administration: During post-marketing surveillance, potentially life-threatening arrhythmia has been reported in a very few patients who received rapid intravenous administration of cefotaxime through a central venous catheter. The recommended time for injection or infusion should be followed.
Effects on Laboratory Tests: As with other cephalosporins a positive Coombs' test has been found in some patients treated with cefotaxime. This phenomenon can interfere with the cross-matching of blood.
Urinary glucose testing with non-specific reducing agents may yield false-positive results. This phenomenon is not seen when a glucose-oxydase specific method is used.
4.5.Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Aminoglycoside antibiotics and diuretics: As with other cephalosporins, cefotaxime may potentiate the nephrotoxic effects of nephrotoxic drugs such as aminoglycosides or potent diuretics (e.g. furosemide). Renal function must be monitored.
Uricosurics: Probenecid interferes with renal tubular transfer of cefotaxime, thereby increasing cefotaxime exposure about 2-fold and reducing renal clearance to about half at therapeutic doses. Due to the large therapeutic index of cefotaxime, no dosage adjustment is needed in patients with normal renal function. Dosage adjustment may be needed in patients with renal impairment.
Interference with Laboratory Tests: A false positive Coombs test may be seen during treatment with cephalosporins. This phenomenon may occur during treatment with cefotaxime and can interfere with blood cross-matching.
A false positive reaction to urinary glucose may occur with copper reduction methods (Benedict's, Fehling's or Clinitest) but not with the use of specific glucose oxidase methods.
There is a potential for mezlocillin and azlocillin to reduce the clearance of cefotaxime.
4.6. Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy: Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B:
Reproduction studies have been performed in pregnant mice given C TAX injection intravenously at doses up to 1200 mg/kg/day (0.4 times the recommended human dose based on mg/m2) or in pregnant rats when administered intravenously at doses up to 1200 mg/kg/day (0.8 times the recommended human dose based on mg/m2). No evidence of embryotoxicity or teratogenicity was seen in these studies. Although cefotaxime has been reported to cross the placental barrier and appear in cord blood, the effect on the human fetus is not known. There are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Lactation: Cefotaxime passes into human breast milk in small amounts and is usually compatible with breast feeding, but careful monitoring of the infant is recommended. Effects on the physiological intestinal flora of the breast-fed infant leading to diarrhoea, colonisation by yeast-like fungi, and sensitisation of the infant cannot be excluded.
Therefore, a decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue therapy taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman.
4.7. Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Cefotaxime has been associated with dizziness, which may affect the ability to drive or operate machinery. There is no evidence that cefotaxime directly impairs the ability to drive or to operate machines. High doses of cefotaxime, particularly in patients with renal insufficiency, may cause encephalopathy (e.g. impairment of consciousness, abnormal movements and convulsions). Patients should be advised not to drive or operate machinery if any such symptoms occur.
4.8.Undesirable effects
Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction
For the treatment of borreliosis, a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction may develop during the first days of treatment.
The occurrence of one or more of the following symptoms has been reported after several week's treatment of borreliosis: skin rash, itching, fever, leucopenia, increase in liver enzymes, difficulty of breathing, joint discomfort.
Hepatobiliary disorders
Increase in liver enzymes (ALAT, ASAT, LDH, gamma-GT and/or alkaline phosphatase) and/or bilirubin have been observed. These laboratory abnormalities may rarely exceed twice the upper limit of the normal range and elicit a pattern of liver injury, usually cholestatic and most often asymptomatic.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions
via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9.Overdose
Symptoms of overdose may largely correspond to the profile of side effects. There is a risk of reversible encephalopathy in cases of administration of high doses of β – lactam antibiotics including cefotaxime.
In case of overdose, cefotaxime must be discontinued, and supportive treatment initiated, which includes measures to accelerate elimination, and symptomatic treatment of adverse reactions (e.g. convulsions). No specific antidote exists. Serum levels of cefotaxime may be reduced by peritoneal dialysis or haemodialysis.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Beta-lactam antibiotics, cephalosporins.
ATC Code: J01D A10
Mode of action
Cefotaxime is a third generation broad spectrum bactericidal cephalosporin antibiotic. The bactericidal properties are due to the inhibitory effect of cefotaxime on bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Mechanisms of resistance
Resistance to Cefotaxime may be due to production of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases that can efficiently hydrolyse the drug, to the induction and/or constitutive expression of AmpC enzymes, to impermeability or to efflux pump mechanisms. More than one of these possible mechanisms may co-exist in a single bacterium.
Breakpoints:
Current MIC breakpoints used to interpret cefotaxime susceptibility data are shown below.
European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) Clinical MIC Breakpoints (V1.1, 31/03/2006)
1. Non-species related breakpoints have been determined mainly on the basis of PK/PD data and are independent of MIC distributions of specific species. They are for use only for species that have not been given a species-specific breakpoint and not for those species where susceptibility testing is not recommended (marked with -- or IE in the table).
2. The cephalosporin breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae will detect resistance mediated by most ESBLs and other clinically important beta-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae. However, some ESBL-producing strains may appear susceptible or intermediate with these breakpoints. Laboratories may want to use a test which specifically screens for the presence of ESBL.
3. Susceptibility of staphylococci to cephalosporins is inferred from the methicillin susceptibility (except ceftazidime which should not be used for staphylococcal infections).
4. Strains with MIC values above the S/I breakpoint are very rare or not yet reported. The identification and antimicrobial susceptibility tests on any such isolate must be repeated and if the result is confirmed the isolate sent to a reference laboratory. Until there is evidence regarding clinical response for confirmed isolates with MIC above the current resistant breakpoint (in italics) they should be reported resistant.-- = Susceptibility testing not recommended as the species is a poor target for therapy with the drug.
IE = There is insufficient evidence that the species in question is a good target for therapy with the drug.
RD = rationale document listing data used by EUCAST for determining breakpoints.
Susceptibility
The prevalence of resistance may vary geographically and with time for selected species and local information on resistance is desirable, particularly when treating severe infections. This information gives only an approximate guidance on the probabilities whether micro-organisms will be susceptible to cefotaxime or not.
Methicillin-(oxacillin) resistant staphylococci (MRSA) are resistant to all currently available β -lactam antibiotics including cefotaxime.
Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae show a variable degree of cross-resistance to cephalosporins such as cefotaxime.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
After a 1000mg intravenous bolus, mean peak plasma concentrations of cefotaxime usually range between 81 and 102 microgram/ml. Doses of 500mg and 2000mg produce plasma concentrations of 38 and 200 micrograms/ml, respectively. There is no accumulation following administration of 1000mg intravenously or 500mg intramuscularly for 10 or 14 days.
The apparent volume of distribution at steady-state of cefotaxime is 21.6 litres/1.73m2 after 1g intravenous 30-minute infusion.
Concentrations of cefotaxime (usually determined by non-selective assay) have been studied in a wide range of human body tissues and fluids. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations are low when the meninges are not inflamed, but are between 3 and 30 microgram/ml in children with meningitis. Cefotaxime usually passes the blood-brain barrier in levels above the minimum inhibitory concentration of common sensitive pathogens when the meninges are inflamed. Concentrations (0.2-5.4 microgram/ml), inhibitory for most Gram-negative bacteria, are attained in purulent sputum, bronchial secretions and pleural fluid after doses of 1 or 2g. Concentrations likely to be effective against most sensitive organisms are similarly attained in female reproductive organs, otitis media effusions, prostatic tissue, interstitial fluid, renal tissue, peritoneal fluid and gall bladder wall, after usual therapeutic doses. High concentrations of cefotaxime and desacetyl-cefotaxime are attained in bile.
Cefotaxime is partially metabolised prior to excretion. The principal metabolite is the microbiologically active product, desacetyl-cefotaxime. Most of a dose of cefotaxime is excreted in the urine - about 60% as unchanged drug and a further 24% as desacetyl-cefotaxime. Plasma clearance is reported to be between 260 and 390ml/minute and renal clearance 145 to 217 ml/minute.
After intravenous administration of cefotaxime to healthy adults, the elimination half-life of the parent compound is 0.9 to 1.14 hours and that of the desacetyl metabolite, about 1.3 hours.
In neonates the pharmacokinetics are influenced by gestational and chronological age, the half-life being prolonged in premature and low birth weight neonates of the same age.
In severe renal dysfunction the elimination half-life of cefotaxime itself is increased minimally to about 2.5 hours, whereas that of desacetyl-cefotaxime is increased to about 10 hours. Total urinary recovery of cefotaxime and its principal metabolite decreases with reduction in renal function.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis
Lifetime studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been conducted. C TAX injection was not mutagenic in the mouse micronucleus test or in the Ames test. C TAX injection did not impair fertility to rats when administered subcutaneously at doses up to 250 mg/kg/day (0.2 times the maximum recommended human dose based on mg/m2) or in mice when administered intravenously at doses up to 2000 mg/kg/day (0.7 times the recommended human dose based on mg/m2).
Nonteratogenic Effects
Use of the drug in women of child-bearing potential requires that the anticipated benefit be weighed against the possible risks. In perinatal and postnatal studies with rats, the pups in the group given 1200 mg/kg/day of C TAX injection were significantly lighter in weight at birth and remained smaller than pups in the control group during the 21 days of nursing.
7.0 Description
C TAX injection (cefotaxime sodium) is a semisynthetic, broad spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic for parenteral administration.
IUPAC Name:
It is the sodium salt of 7-[2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl) glyoxylamido]-3- (hydroxymethyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate 72 (Z)-(o-methyloxime), acetate (ester).
The molecular formula of cefotaxime is C16H16N5NaO7S2 Molecular weight is 477.442 g/mol.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
1.Incompatibilities
Cefotaxime sodium should not be mixed with alkaline solutions such as sodium bicarbonate injection or solutions containing aminophylline.
Cefotaxime should not be admixed with aminoglycosides. If they are used concurrently they should be administered in separate sites.
2.Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
3. Packaging information
C-Tax 250: A vial of 250 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
C-Tax 500: A vial of 500 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
C-Tax 1.0 g: A vial of 1 g with SWFI IP 5 ml.
4. Storage and handing instructions
Store in a cool & dry place. Protect from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
After reconstitution, do not use in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including C-Tax injection should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When C-Tax injection is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed.
Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by C-Tax injection or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
12.0 Date of revision
17th Sept. 2024
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or your pharmacist.
In this leaflet:
- What C-Tax Injection is and what it is used for.
- Before you are given C-Tax Injection.
- How C-Tax Injection is given.
- Possible side effects.
- How to store C-Tax Injection Further information.
The name of your medicine is “Cefotaxime sodium for injection” (referred to as C-Tax Injection throughout this leaflet).
1. What C-tax Injection is and What It is Used for
Cefotaxime is an antibiotic. It belongs to a group of antibiotics that are called cephalosporins. These types of antibiotic are similar to penicillin.
Cefotaxime kills bacteria and it can be used to treat infections of the:
- Kidneys and bladder
- Blood (septicaemia)
- Skin and flesh immediately under the skin
- Bones
- Heart valves
- Brain (meningitis)
- Abdomen (peritonitis)
- Some sexually transmitted infections (gonorrhoea)
It can also be used to prevent and treat infections following surgical operations.
2. Before You Are Given C-tax Injection
You should not be given Cefotaxime injection if:
- you are allergic (hypersensitive) to cefotaxime
- you are allergic to any similar antibiotics (known as “cephalosporins”)
- you have ever had a serious allergic reaction when given penicillin or similar antibiotics
- you are allergic to lidocaine
Tell your doctor or nurse if any of the above apply to you.
Before you are given C-Tax injection
You must tell the doctor or nurse if any of the following apply to you:
you have a history of allergies or asthma
you are on a low sodium diet
you have a heart or kidney disorder
you are having any blood or urine tests
you have a history of gastro-intestinal problems e.g. colitis, which causes diarrhoea containing blood.
Taking other medicines
Tell the doctor or nurse if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- the contraceptive pill (in which case you will need to take extra contraceptive precautions such as using a condom)
- any diuretic medicine (“water tablets”) e.g. furosemide
- another antibiotic e.g. chloramphenicol or aminoglycoside antibiotics probenecid (for gout)
Please tell your doctor if you are taking, or have recently taken, any other medicines including any that you may have bought without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant, think you might be pregnant or are breastfeeding, you must tell your doctor before you are given this medicine.
Driving and using machines
If you are given high doses of cefotaxime, you may feel dizzy/drowsy or fall asleep or experience convulsions (fits) or unusual body movements. If this happens, you should not drive or operate machinery.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Cefotaxime injection
C-Tax Injection contains approximately 50 mg (2.09 mmol) of sodium per 1g dose. This should be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet. Tell your doctor or nurse if you are on a low sodium diet.
3. How C-tax Injection is Given
C-Tax Injection is supplied as a powder so before it can be given it must be diluted and made into a solution. Your doctor or nurse normally does this. They will inject this directly into a vein (intravenous) or muscle (intramuscular). It may also be given by an intravenous infusion (“drip”).
Your doctor will decide how much you need and how often the injections should be given. The usual doses are given below but doctors may prescribe different doses depending on the severity and type of your infection, your weight, your age and how well your kidneys are working.
Treatment with C-Tax injection is usually continued for 2-3 days after you start to recover from your illness or after your operation.
Adults and children over 12 years old:
The usual dose is 1 g every twelve hours. In some patients where infections are severe, the doctor may give a higher dose up to 12 g every day. For the treatment of gonorrhoea, a single 500mg dose is usually given. To prevent an infection after surgery, 1 -2 g is given before the operation. A second dose may be needed after the operation.
Infants and children up to 12 years old:
The usual daily dose is 50 mg to 100 mg Cefotaxime per kilogram of their bodyweight. This is usually split into 2 doses each day. Severely ill children may receive up to 200 mg per kg bodyweight daily (to a maximum of 6 g daily), split into 3 separate doses.
Young babies (new-born):
The daily dose should not normally exceed 50 mg Cefotaxime per kg of their bodyweight.
Patients with kidney problems:
Lower doses may be given if you have severe kidney problems. Patients on dialysis machines will be monitored for the correct dose.
If you think you have missed an injection
This is unlikely as you will probably receive this medicine in hospital. If you think you have missed a dose, speak to your doctor or nurse.
If you have been given more of this medicine than you should
This is unlikely to happen but if it does, the doctor will treat any symptoms that follow.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, C-Tax Injection can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
As with other antibiotics, some people find they have an allergy to it. Tell your doctor immediately if any of the following rare symptoms occur:
- Sudden wheeziness and tightness of chest
- Swelling of eyelids, face, lips or throat
- Skin lumps or “hives” (nettle rash)
- Severe skin rashes with itching
- Serious illness with blistering of the skin, mouth, eyes and genitals
- Loss of consciousness, abnormal movements or convulsions (fits)
Antibiotic treatment can affect the normal bacteria in the gut, causing new infection (colitis). You should tell your doctor immediately if you develop diarrhoea.
The following side effects may occur in some patients treated with C-Tax injection. Tell your doctor if any become troublesome:
Very common side effects (probably affecting more than 1 in 10 people)
- pain at the injection site
Uncommon side effects (probably affecting less than 1 in 100 patients)
- reduction in blood platelets which increases risk of bruising or bleeding
- reduction in number of white blood cells which makes infections more likely
- increase in number of white blood cells
- fever
- increase in liver enzymes and/or bilirubin
- kidney problems
- skin rash, itching, ‘hives’ (nettle rash)
- difficulty breathing
- convulsions (fits)
- diarrhoea
- redness and swelling at injection site
Side effects occurring with unknown frequency
- secondary infections
- serious allergic reactions which may cause difficulty in breathing or dizziness
- serious allergic reaction which causes swelling of the face or throat
- difficulty in breathing or wheezing
- headache
- dizziness
- loss of consciousness, abnormal movements
- feeling sick (nausea)
- being sick (vomiting)
- stomach pains
- diarrhoea containing blood
- inflammation of the liver (hepatitis)
- skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow (jaundice)
- painful joints
- irregular heart rhythm
- inflammation of the kidneys which may cause dark discolouration of urine, cloudy/bloody urine, or any change in your urine output.
Treatment with high doses of Cefotaxime, particularly in patients with kidney problems, has been known to cause loss of consciousness, abnormal movements and convulsions (“fits”).
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to Store C-tax Injection
Keep out of the reach and sight of children. Do not use C-Tax injection after the expiry date which is printed on the label and carton. Do not store above 25°C. Keep the vial in the outer carton. Your doctor, pharmacist or nurse will know how to store C-Tax injection properly.
6. Further Information
What C-Tax injection contains:
Each vial contains 250 mg, 500mg or 1g Cefotaxime (as Cefotaxime sodium).
There are no other ingredients.
C-Tax 250:
A vial of 250 mg with Sterile Water for Injection -5 ml.
C-Tax 500:
A vial of 500 mg with Sterile Water for Injection-- 5 ml. C-Tax 1.0 g:
A vial of 1 g with Sterile Water for Injection- 5 ml.
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd.
Zuventus House, Plot Y2, CTS No.: 358/A2,
Near Nahur Railway Station,
Nahur (W), Mumbai, 400078 Maharashtra, India