La-Mika Injection
1.0 Generic name
Amikacin injection
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
La-Mika® 100 Injection
Each vial (2ml) contains:
Amikacin Sulphate IP
equivalent to Amikacin 100 mg,
Methylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.08 % w/v
Propylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.02 % w/v
Water for Injection IP q.s.
LaMika® 250 Injection
Each vial (2ml) contains:
Amikacin Sulphate IP
equivalent to Amikacin 250 mg,
Methylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.08 % w/v
Propylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.02 % w/v
Water for Injection IP q.s.
LaMika® 500 Injection
Each vial (2ml) contains:
Amikacin Sulphate IP equivalent to Amikacin 500 mg,
Methylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.08 % w/v
Propylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.02 % w/v
Water for Injection IP q.s.
3.0 Pharmaceutical form and Strength
Injection 125 mg/250 mg/500 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment of serious infections due to amikacin sensitive organisms.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults and adolescents over 12 years
The recommended intramuscular or intravenous dose for adults and adolescents with normal renal function (creatinine clearance ≥50 mg/min) is 15 mg/kg/day given either as a single daily dose or as several equal doses (e.g. 7.5 mg/kg all 12 hours, or 5 mg/kg every 8 hours). The total daily dose should not exceed 1.5 g. For endocarditis and febrile neutropenic patients, dosing should be done twice a day, as there is insufficient data for once-daily dosing.
Children from 4 weeks to 12 years
The recommended intramuscular or intravenous (slow intravenous infusion) dosage for children with normal renal function is 15-20 mg/kg/day, given either as a single daily dose of 15-20 mg/kg or divided into two doses of 7.5 mg/kg every 12 hours.
For endocarditis and febrile neutropenic patients, dosing should be done twice a day, as there is insufficient data for once-daily dosing.
Neonates
An initial dose of 10 mg/kg, then 7.5 mg/kg every 12 hours.
Preterm infants
The recommended dose for preterm infants is 7.5 mg/kg every 12 hours.
Dosage in elderly patients (≥ 65 years)
Renal function should be taken into account in elderly patients.
Life-threatening infections and/or those caused by Pseudomonas
The adult dose may be increased to 500 mg every eight hours but should neither exceed 1.5 g/day nor be administered for a period longer than 10 days. A maximum total adult dose of 1.5 g should not be exceeded.
Urinary tract infections (other than pseudomonal infections)
7.5 mg/kg/day in two equally divided doses (equivalent to 250 mg twice daily in adults). As the activity of amikacin is enhanced by increasing the pH, a urinary alkalizing agent may be administered concurrently.
Other routes of administration
Amikacin in concentrations of 0.25 % (2.5 mg/ml) may be used satisfactorily as an irrigating solution in abscess cavities, the pleural space, the peritoneum and the cerebral ventricles.
Intraperitoneal use
Following exploration for established peritonitis, or after peritoneal contamination due to faecal spill during surgery, Amikacin may be used as an irrigant after recovery from anaesthesia in concentrations of 0.25 % (2.5 mg/ml). If instillation is desired in adults, a single dose of 500 mg is diluted in 20 ml of sterile distilled water and may be instilled through a polyethylene catheter sutured into the wound at closure. If possible, instillation should be postponed until the patient has fully recovered from the effects of anaesthesia and muscle-relaxing drugs.
Monitoring
The renal function status should be evaluated by measuring the serum creatinine concentration or preferably by estimation of creatinine clearance. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is far less reliable for this purpose. Assessment of renal function should be performed at the start of therapy and should be re-evaluated at regular intervals during treatment.
Amikacin concentrations in serum should be measured in all patients receiving parenteral amikacin and must be measured in obesity, if high doses are being given, the elderly and in cystic fibrosis. Both peak and trough serum concentrations should be measured intermittently during therapy to ensure adequate but not excessive serum levels. In patients receiving multiple daily dosing peak concentrations (30-90 minutes after injection) of above 35 μg/ml and trough concentrations (just before the next dose) of above 10 μg/ml should be avoided.
In patients receiving once daily (or extended interval) dosing pre-dose ('trough') concentration should be less than 5 mcg/ml. Peak concentrations (approximately 60 minutes after administration) may exceed 35 mcg/ml.
If the pre-dose ('trough') concentration is high, the interval between doses must be increased. If the post-dose ('peak') concentration is high, the dose must be decreased.
Auditory and vestibular function should also be monitored during treatment, in particular if longer treatment duration (>7-10 days) is considered.
Dosage in renal impairment
In patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance <50 ml/min) the recommended dose has to be decreased and adjusted to the renal function. This can be achieved by increasing the dose interval and/or reducing the dose.
In all patients with renal impairment, serum amikacin peak and trough concentration and renal function must be monitored regularly and the dose regimen altered as necessary.
Once daily/extended interval dosing
Patients with renal impairment in whom once daily dosing would be considered appropriate if their renal function were normal may receive extended interval dosing.
The initial dose may be the same as in normal renal function. The dose interval should be at least 24 hours and extended according to the degree of renal impairment and the results of serum amikacin level measurements.
In severe renal impairment, the initial dose may have to be reduced in addition.
Once daily or extended interval dosing should be avoided in patients with a creatinine clearance less than 20 ml/minute.
A once daily/extended interval dose regimen should be avoided in children over 1 month of age with a creatinine clearance less than 20 ml/minute/1.73 m2.
Reduced dose at fixed intervals
If patients with renal impairment are given amikacin at fixed time intervals, the dose must be reduced. In these patients, the serum amikacin concentration should be measured to ensure accurate administration and to avoid excessive serum concentrations. If a determination of serum concentration is not possible and the patient's condition is stable, serum creatinine and creatinine clearance rates are the most readily available indicators of the extent of renal dysfunction and the consequent reduction in dose.
As renal function may alter appreciably during therapy, the serum creatinine should be checked frequently and the dosage regimen modified as necessary.
Multiple daily dosing
In patients with renal impairment in whom multiple daily dosing at fixed intervals would be considered appropriate if their renal function were normal, the dose must be reduced while the dose interval is maintained. Serum amikacin concentrations should be measured and creatinine clearance should be estimated regularly.
Treatment duration
At recommended dosages, infections caused by susceptible pathogens should respond to therapy within 24-48 hours. If clinical response does not occur within 3-5 days, therapy should be discontinued and the antibiotic susceptibility pattern of the invading organism should be rechecked. If necessary, alternative therapy should be considered. Failure of therapy may be due to the resistance of the organism or to septic locus requiring surgical drainage.
The average duration of treatment is 7-10 days. For all routes of administration, the maximum daily dose should not exceed 15-20 mg/kg/day. If prolonged treatment is required, it should be carried out after reviewing the necessity of using amikacin, determination of serum amikacin concentrations and additionally monitoring of renal, auditory and vestibular functions as closely as possible daily.
Method of administration
IM use or IV use after dilution.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or other aminoglycoside antibiotics.
- Due to the known cross sensitivities in this class of drugs, a history of hypersensitivity or serious toxic reactions to aminoglycosides may be a contraindication to all aminoglycosides.
- Because of its sulphate content, Amikacin must not be used in asthmatics with sulphate hypersensitivity.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions
Neuromuscular toxicity
Neuromuscular blockade and respiratory paresis have been reported following parenteral injection, topical lavage (such as orthopaedic and abdominal irrigation, or with local empyema treatment) or after oral administration of aminoglycosides. The risk of respiratory paresis when administering aminoglycosides irrespective of the route of administration should be considered, especially in patients receiving anaesthetics or neuromuscular blockers. Antidote in neuromuscular blockade: supply of calcium in ionized form (to relieve respiratory paralysis) and neostigmine. Mechanical ventilation may be necessary. In animal studies, neuromuscular blocks and myoparesis were found after administration of high doses of amikacin.
Aminoglycosides should be used with extreme caution in patients with myasthenia gravis as the curare-like effect on the neuromuscular junction may increase myasthenia with the potential for respiratory failure.
Aminoglycosides should be used with caution in patients with muscular disorders such as parkinsonism, since these drugs may aggravate muscle weakness because of their potential curare-like effect on the neuromuscular junction.
Nephrotoxicity and Ototoxicity
Amikacin is potentially nephrotoxic and ototoxic; therefore, patients must be carefully monitored clinically. Particular caution should be applied to patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency, or pre-existing hearing or vestibular damage. Safety for treatment periods which are longer than 14 days has not been established.
Precautions regarding the dose should be observed and adequate hydration maintained. Neurotoxicity occurring in patients treated with aminoglycosides is manifested as vestibular and/or bilateral ototoxicity.
Ototoxicity:
The risk of aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity is greater in patients with impaired renal function, and in those who receive high doses, or in those whose therapy is prolonged over 5-7 days. High frequency deafness usually occurs first and can be detected only by audiometric testing. Vertigo or dizziness may occur and may be evidence of vestibular injury.
Other manifestations of neurotoxicity include numbness, tingling of the skin, muscle twitching and muscle spasms. At the first sign of hearing and/or balance disorders, therapy with amikacin should be discontinued.
The risk of ototoxicity due to aminoglycosides increases with the level of exposure either through consistently high peak serum concentrations or high serum trough concentrations. Patients who develop auditory or vestibular damage may not have any symptoms during therapy that may alert them to eighth nerve damage, and total or partial irreversible bilateral deafness or disabling vertigo may occur after the drug has been discontinued.
Aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity is usually irreversible.
Evidence of ototoxicity (dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, roaring in the ears and hearing loss) or nephrotoxicity requires discontinuation of the drug or dosage adjustment.
The use of amikacin in patients with a history of allergy to aminoglycosides or in patients who may have subclinical renal or eighth nerve damage induced by prior administration of nephrotoxic and/or ototoxic agents such as streptomycin, dihydrostreptomycin, gentamicin, tobramycin, kanamycin, bekanamycin, neomycin, polymyxin B, colistin, cephaloridine, or viomycin should be considered with caution, as toxicity may be additive.
In these patients amikacin should be used only if, in the opinion of the physician, therapeutic advantages outweigh the potential risks.
Nephrotoxicity
Aminoglycosides are potentially nephrotoxic. Renal toxicity appears independent of plasma obtained at the peak (Cmax). The risk of nephrotoxicity is increased in patients with impaired renal function and in patients receiving high doses or prolonged drug therapy.
Patients should be well hydrated during treatment and renal function should be assessed by the usual methods prior to starting therapy and daily during the course of treatment. A reduction of dosage is required if evidence of renal dysfunction occurs, such as presence of urinary casts, white or red cells, albuminuria, decreased creatinine clearance, decreased urine specific gravity, increased BUN, serum creatinine, or oliguria. If azotemia increases, or if a progressive decrease in urinary output occurs, treatment should be stopped.
Aminoglycosides may be inactivated by betalactams. Inactivation may continue in samples (serum, cerebrospinal fluid, etc.) taken for laboratory testing and then interfere with aminoglycoside level assays. The samples should therefore be adequately treated after collection (immediate determination, storage in the freezer or addition of beta-lactamase).
Concurrent and/or sequential systemic, oral, or topical use of other neurotoxic or nephrotoxic products, particularly bacitracin, cisplatin, amphotericin B, cephaloridine, paromomycin, viomycin, polymyxin B, colistin, vancomycin, or other aminoglycosides, should be avoided. Other factors that may increase risk of toxicity are advanced age and dehydration.
Other
Aminoglycosides are quickly and almost totally absorbed when they are applied topically, except to the urinary bladder, in association with surgical procedures.
Irreversible deafness, renal failure and death due to neuromuscular blockade have been reported following irrigation of both small and large surgical fields with an aminoglycoside preparation.
Prolonged antibiotic use may occasionally lead to overgrowth of resistant pathogens. The patient should be constantly monitored in this regard. Should a superinfection occur during therapy, appropriate measures must be taken.
Macular infarction sometimes leading to permanent loss of vision has been reported following intravitreous administration (injection into the eye) of amikacin.
Paediatric use
Aminoglycosides should be used with caution in premature and neonatal infants because of the renal immaturity of these patients and the resulting prolongation of serum half-life of these drugs.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Concurrent or serial use with other neurotoxic, ototoxic or nephrotoxic agents, particularly bacitracin, cisplatin, amphotericin B, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, cephaloridine, paromomycin, viomycin, colistimethate/colistin, vancomycin, or other aminoglycosides should be avoided both systemically and topically because of the potential for additive effects. Increased nephrotoxicity has been reported following concomitant parenteral administration of aminoglycoside antibiotics and cephalosporins. Concomitant cephalosporin use may spuriously elevate creatinine serum level determinations.
The risk of ototoxicity is increased when amikacin is used in conjunction with rapidly acting diuretic drugs, particularly when the diuretic is administered intravenously.
Diuretics may enhance aminoglycoside toxicity by altering antibiotic concentrations in serum and tissue. Such agents include furosemide and ethacrynic acid which is itself an ototoxic agent. Irreversible deafness may result.
There is an increased risk of nephrotoxicity and possible ototoxicity when aminoglycosides are co-administered with platinum compounds.
The use of amikacin is not recommended in patients receiving anaesthetics or musclerelaxing drugs (such as volatile anaesthetics, d-tubocurarine, succinylcholine, decamethonium, atracurium, rocuronium, vecuronium) or in patients receiving massive transfusions of citrate-anticoagulated blood) as neuromuscular blockade and consequent respiratory depression may occur. If blockade occurs, calcium salts may reverse this phenomenon.
Indomethacin may increase the plasma concentration of amikacin in neonates.
In patients with severely impaired renal function, a reduction in activity of aminoglycosides may occur with concomitant use of penicillin-type drugs.
In vitro admixture of aminoglycosides with beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillins or cephalosporins) may result in significant mutual inactivation. A reduction in serum activity may also occur when an aminoglycoside or penicillin-type drug is administered in vivo by separate routes. Inactivation of the aminoglycoside is clinically significant only in patients with severely impaired renal function.
Inactivation may continue in specimens of body fluids collected for assay, resulting in inaccurate aminoglycoside readings. Such specimens should be properly handled (assayed promptly, frozen, or treated with beta-lactamase).
There is an increased risk of hypocalcaemia when aminoglycosides are administered with bisphosphonates.
There is an increased risk of nephrotoxicity and possibly of ototoxicity when aminoglycosides are administered with platinum compounds.
Concomitantly administered thiamine (vitamin B1) may be destroyed by the reactive sodium metabisulfite component of the amikacin sulphate formulation.
Sulphate is a very reactive compound. Therefore, mixtures with other medicinal products should be avoided.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Amikacin should be used in pregnant women and newborns only if clearly indicated and under medical supervision.
There is limited data on the use of aminoglycosides in pregnancy. Aminoglycosides can affect the development of the embryo/foetus in the womb. Aminoglycosides cross the placental barrier and there have been many reports of total, irreversible, bilateral congenital deafness in children whose mothers were treated with streptomycin during pregnancy.
Although adverse reactions to the unborn or neonate in pregnant women who have been treated with other aminoglycosides have not been reported, there is potential for harm.
If a pregnant patient is to be treated or becomes pregnant during treatment, medical advice should be provided on the risk of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Breast-feeding
It is not known if amikacin passes into the breast milk. The decision should be made to either stop breastfeeding or stop the therapy.
Fertility
In reproduction toxicity studies in mice and rats, no effects on fertility or foetal toxicity were reported.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the ability to drive and the use of machines have been performed. However, the occurrence of some side effects may affect the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
4.8 Undesirable effects
All aminoglycosides have oto-, nephro- and neurotoxic potential.
The risk of these side effects is greater in patients with already impaired renal function, in patients receiving more than the recommended doses, prolonged therapy and in patients treated with other ototoxic or nephrotoxic drugs.
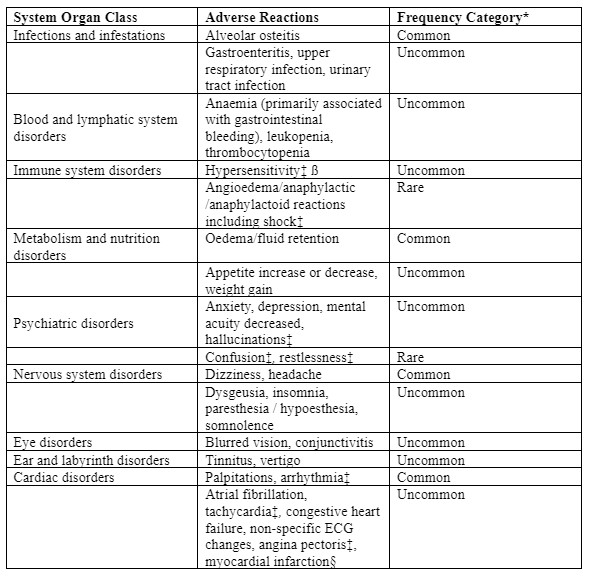
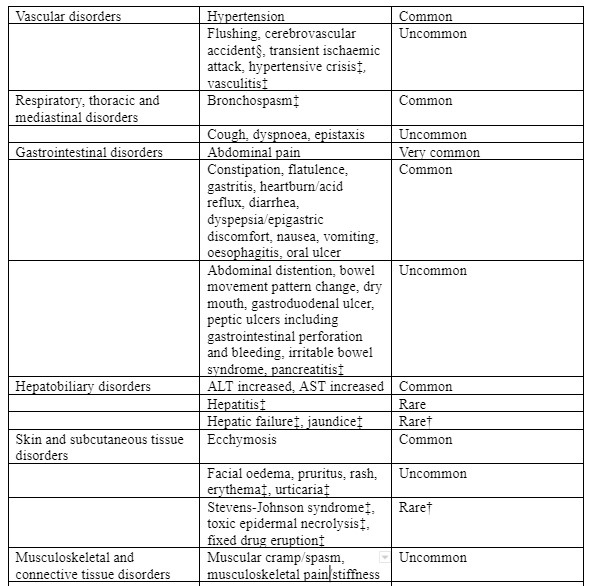
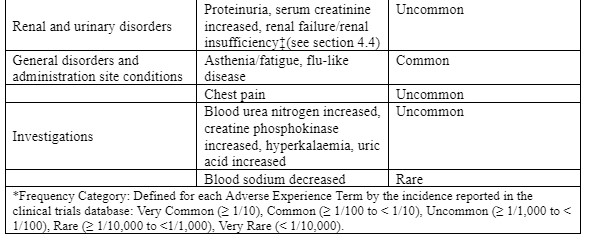
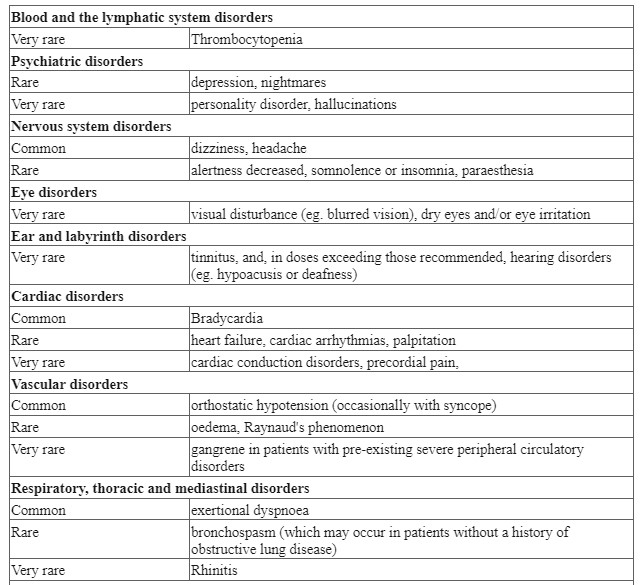
| MedDRA system organ class | Frequency | Adverse event |
|---|---|---|
| Infections and infestations | Uncommon | Super infection or colonization with resistant bacteria or yeasts. |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Rare | Anaemia, eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia |
| Immune system disorders | Not known | Anaphylactic response (anaphylactic reaction, anaphylactic shock and anaphylactic reaction), hypersensitivity |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Rare | Hypomagnesemia |
| Nervous system disorders | Rare Not known | Tremor, paraesthesia, headache, balance disorders headache, balance Paresisa |
| Eye disorders | Rare | Blindness**, retinal infarct, |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders | Common , Not known | Tinnitusa, hypoacusis,Chochlear damage Deafness, sensory deafness |
| Vascular disorders | Rare | Hypotonia, thrombophlebitis |
| Cardiac disorders | Rare | Tachycardia and myocarditis |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Not known | Apnoea, bronchospasm |
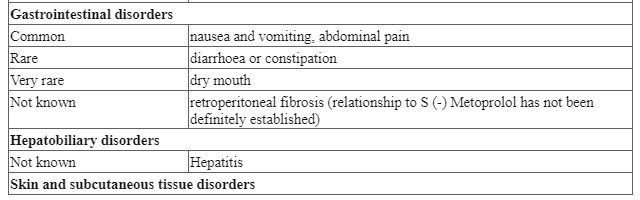
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Uncommon | Vomiting, nausea |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | Rare | Elevation of liver enzymes in plasma (SGOT, SGPT, LDH, alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Uncommon Rare | Rash Pruritus, urticaria |
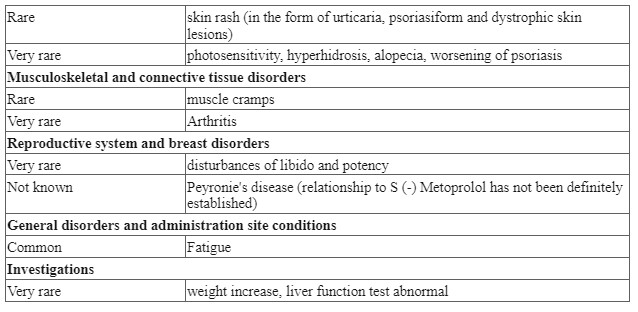
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Rare | Arthralgia, myokymia |
| Renal and urinary disorders | Common Not known | Nephrotoxicity, oliguria Increase in serum creatinine, albuminuria, azotemia, red blood cells in the urine, white blood cells in the urine, cells in the urine Acute renal failure |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Rare Not known | Fever Pain in the injection site** |
* Changes in renal function are usually reversible at the end of therapy. ** Amikacin is not intended for administration to the vitreous body. When amikacin was injected directly into the eye, maculopathies were observed, occasionally leading to complete loss of vision.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorization of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Significant risk of overdose is a potential nephro, oto and neurotoxic (neuromuscular blockade) effect. Respiratory neuromuscular blockade should be appropriately treated, including the administration of calcium in ionised form (for example as gluconate or lactobionate in 10-20 % solution). In case of overdose or toxic reactions, amikacin can be removed by peritoneal or hemodialysis. Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration also leads to a reduction of amikacin. In neonates an exchange transfusion may be considered.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action / Pharmacodynamic properties
The mechanism of action of amikacin is due to a disruption of protein biosynthesis on the bacterial ribosome by interaction with the rRNA and subsequent inhibition of translation. This results in a bactericidal effect.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic Properties
After IM injection, amikacin is well tolerated locally and rapidly absorbed. After administration of 250 mg amikacin IM average serum peak concentrations of 11 μg/ml are achieved within one hour when amikacin 21 μg/ml is administered. I.V. short infusion of 500 mg amikacin results in an average serum concentration of 38 μg/ml (end of infusion). After 1 hour, 18 μg/ml were still detectable. In elderly patients (with mean creatinine clearance of 64 ml/min) the blood levels are 55 μg/ml after a 30-minute infusion of 15 mg/kg, 5.4 μg/ml after 12 hours and 1.3 μg/ml after 24 hours.
Serum half-life in patients with normal renal function is 2.4 hours, with an average volume of distribution of 24 litres and about 28 % of body weight. Plasma protein binding ranges from 0-11 %. The average serum clearance rate is 100 ml/min; The renal clearance rate in normal renal function is 94 ml/min. Amikacin is not metabolized and excreted almost exclusively by glomerular filtration. In normal renal function, approximately 91 % of the IM administered dose is excreted within the first 8 hours via urine in active form and 98 % within 24 hours.
Amikacin is removable by both peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis. By peritoneal dialysis (patients without infection) about 20 % of the administered amikacin dose could be removed within 8-12 hours. Hemodialysis is much more effective. Depending on the dialysis method, either 50 % (range 29-81 %) of the administered dose was removed within 4 hours or 40-80 % was removed within 8 hours.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
No long-term studies have been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential. Studies in rats have shown that daily doses up to 10 times recommended dose for humans did not cause any adverse effects on male and female fertility.
7.0 Description
Amikacin, (as the sulphate) is a semi-synthetic aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from kanamycin.
D-Streptamine,O-3-amino-3-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-[6-amino-6-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-N1-(4-amino-2-hydroxy-1-oxobutyl)-2-deoxy-, (S)-, sulphate (1:2) (salt).

Chemical Structure: C22H43N5O13 • 2H2SO4
Molecular weight: 781.75
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Aminoglycosides such as amikacin should not be combined with other medicines, but must be administered separately.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on package
8.3 Packaging information
2ml Injection vial containing amikacin
125 mg/250 mg/500 mg
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 300C. Protect from light and moisture. Don’t freeze. Keep out of reach of children. Do not use if solution is not clear or has particulate matter in vial.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Patients should be counselled that antibacterial drugs including amikacin sulphate injection should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When amikacin sulphate injection is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by amikacin sulphate injection or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Patients should be counselled that diarrhoea is a common problem caused by antibiotics, and it usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as 2 or more months after having taken their last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet:
1. What La-Mika® is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take La-Mika®
3. How to take La-Mika®
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store La-Mika®
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What La-Mika® is and what it is used for
La-Mika® Injection is one of a group of antibiotic medicines called ‘aminoglycosides’. La-Mika® Injection is used in the treatment of serious infections caused by bacteria sensitive to amikacin.
2. What you need to know before you take La-Mika®
Do not take LaMika®, if
you have shown signs of hypersensitivity (severe allergy) to amikacin, or any of the other ingredients, in the past
you suffer from a disorder called myasthenia gravis (severe weakness of certain muscles of the body).
Tell your doctor if any of the above applies to you before this medicine is used.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before using La-Mika® Injection
- if you have kidney problems
- if you have hearing difficulties or tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears)
- if you have shown signs of allergy to any of the antibiotics related to amikacin (aminoglycosides) in the past
Tell your doctor if any of the above applies to you before this medicine is used. Children
Amikacin should be used with caution in premature and neonatal infants.
Other medicines and La-Mika®
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken or might take/use any other medicines. Special care is needed if you are taking/using other medicines, as some could interact with amikacin for example:
- Diuretics (water tablets) such as furosemide and ethacrynic acid
- Other antibiotics that can affect your kidneys, hearing or balance
- Anaesthetics or muscle-relaxing drugs
- Indomethacin (an anti-inflammatory medicine)
- Other antibiotics called beta-lactamases such as penicillins or cephalosporins
- Bisphosphonates; drugs used to treat loss of bone mass
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
- Platinum compounds used in chemotherapy such as cisplatin
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine. Your doctor will only use this medicine if the expected benefits outweigh any potential risk to your baby.
Driving and using machines
Do not drive or use machines if you experience any side effect (e.g. dizziness) which may lessen your ability to do so.
3. How to use La-Mika®
This medicine is usually injected into a muscle. It may also be given into a vein, either as an injection or (following dilution) as an infusion (drip). Amikacin can also be given into the peritoneum (abdominal cavity) during surgery, and can be used to wash out abscess cavities, the lung cavity and brain cavities.
Your doctor will ensure you are well hydrated before and during treatment. Dose
Your doctor will work out the correct dose of amikacin for you and how often it must be given. This may require blood tests before treatment. The dose will depend upon your age, the infection you have, how well your kidneys are working, if you have poor hearing and any other medicines you may be taking. It will usually be given to you two or three times a day, for up to 10 days.
Adults and children over 12 years
The usual dose is 15 mg per kg per day which is administered as a single dose or divided into two equal doses of 7.5 mg per kg administered every 12 hours. The total dose should not exceed 1.5 g. When treatment is given in to a vein it is usually administered over a 30 to 60 minute period.
Children up to 12 years
The usual dose is 15 – 20 mg per kg of body weight once a day or divided into two equal doses of 7.5 mg per kg which is administered every 12 hours. Neonates
The initial dose is 10 mg per kg of body weight followed by 7.5 mg per kg every 12 hours. Premature infants
The recommended dosing in premature babies is 7.5 mg per kg every 12 hours.
During treatment you may undergo blood tests and be asked to provide urine samples. You will possibly also have hearing tests before and during treatment to look for signs of side effects. Your doctor may change your dose depending upon the results of these tests.
If you are given too much or too little La-Mika® Injection
This medicine will be given to you in a hospital, under the supervision of a doctor. It is unlikely that you will be given too much or too little, however, tell your doctor or nurse if you have any concerns.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If any of the following happens, tell your doctor immediately as these are all serious. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation.
Rare side-effects may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people are listed below:
- Ringing in your ears or loss of hearing
- Decrease in the amount of urine you produce
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from available data are listed below:
- Severe allergic reaction - you may experience a sudden itchy rash (hives), swelling of the hands, feet, ankles, face, lips, mouth or throat (which may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing), and you may feel you are going to faint
- Paralysis
- Deafness
- Sudden loss of breathing
- Severe kidney failure
These are serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention.
If any of the following happens, tell your doctor as soon as possible:
Uncommon side-effects may affect up to 1 in 100 people are listed below:
- Skin rash
- Nausea and vomiting
- An excessive build-up of bacteria or yeast which are resistant to amikacin
Rare side-effects may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people are listed below:
- Dizziness or vertigo (spinning sensation)
- Headache
- Fever
- Unusually low amount of red blood cells in the blood (anaemia) or excessive amounts of the white blood cells known as eosinophils in the blood (eosinophilia)
- Low levels of magnesium in the blood
- Abnormal tingling or ‘pins and needles’ sensation
- Muscle tremors
- Joint pain
- Low blood pressure
- Itching or hives
Amikacin may lead to changes in your kidney function. Your doctor may take blood and urine samples to monitor for changes such as increased levels of creatinine or nitrogen in the blood and protein or red/white blood cells in urine. Your doctor may also ask you to undergo hearing tests.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor.
Reporting of side effects
Reporting of side effects If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store La-Mika®
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children The vials should be stored at or below 25°C. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month. Unused portions of opened vials must not be stored for later use. Prepared injections or infusions should be used immediately, however, if this is not possible they can be stored for up to 24 hours.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
La-Mika® 100 Injection
Each vial contains: Amikacin Sulphate IP equivalent to Amikacin 100 mg,
Methylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.08 % w/v
Propylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.02 % w/v
Water for Injection IP q.s.
La-Mika® 250 Injection
Each 2 ml contains: Amikacin Sulphate IP equivalent to Amikacin 250 mg,
Methylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.08 % w/v
Propylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.02 % w/v
Water for Injection IP q.s.
La-Mika® 500 Injection
Each 2 ml contains:
Amikacin Sulphate IP
equivalent to Amikacin 500 mg,
Methylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.04 % w/v,
Propylparaben IP (as preservatives) 0.01 % w/v
Water for Injection IPq.s.
Packaging
2ml vial